What is Aluminium?
Aluminium is a chemical element that belongs to the metal group, also known as the boron group. It is a nonferrous metal abundant in the earth’s crust. In nature, aluminium does not occur in metallic form, but its compounds can be found on vegetation, animals, and in almost all rocks on earth.

Where is Aluminum obtained?
You cannot find pure aluminium in nature. The production of aluminum starts with bauxite ore consisting of hydrate aluminum oxide, silica, and iron oxide. To be able to produce at least two tonnes of alumina, it would require at least five tonnes of bauxite ore.

History of Aluminium
Alum has long been used for tanning, dyeing, and stopping bleeding. In the 1750s, Andreas Marggraf, a German chemist, noticed that he could create a substance out of alum by using an alkali solution. He was the same person who isolated zinc in 1746.
Classification, Properties and Characteristics of Aluminium
One of the cardinal characteristics of aluminum is its silvery white color. It is also paramagnetic, which means that its magnetic ability is very weak under normal conditions. Although it does not stick to magnets, it is a very good conductor of electricity. It is ductile and low in density.
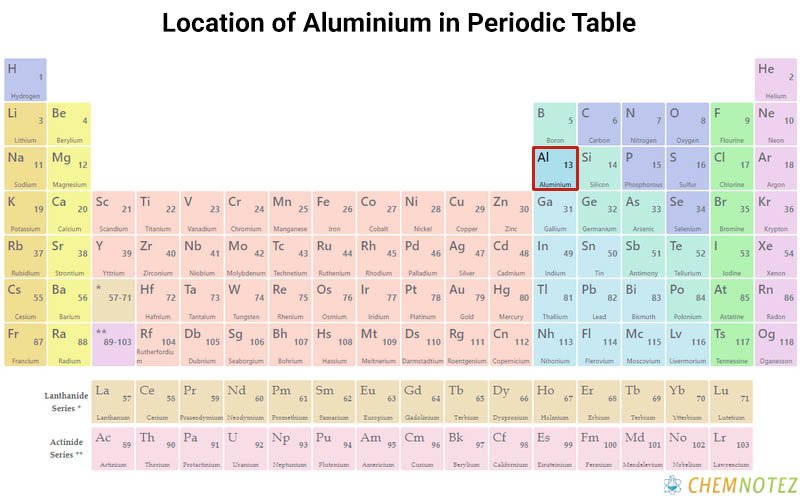
Lewis Dot Structure of Aluminium
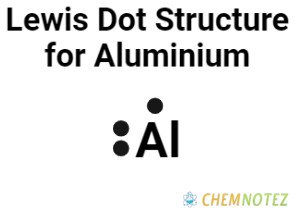
Bohr’s Atomic Model
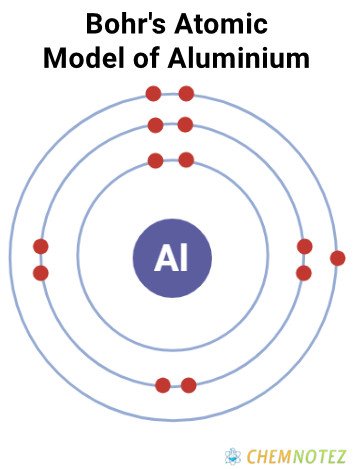
Atomic Data of Aluminium
Physical Properties of Aluminium
| Color | silvery white |
| Odor | odorless |
| Taste | tasteless |
| Atomic Mass | 26.982 |
| Weight | 26.981539 u |
| Density | 2.70 |
| Atomic Radius | 1.43 Å |
| Ionization Energy | 5.9858 eV |
| Covalent Radius | 1.24 Å |
| Ionic Radius | 51 (+3e) |
| Electronic Gain Enthalpy | unknown |
| Electron Negativity | 1.610 |
| Electron Affinity | 42.5 kJ/mol |
| Melting Point | 660.323°C, 1220.581°F, 933.473 K |
| Boiling Point | 2519°C, 4566°F, 2792 K |
Chemical Properties of Aluminium
| Atomic Number | 13 |
| Group | 13 |
| Period | 3 |
| Block | p |
| Electronic Configuration | [Ne] 3s23p1 |
| Combustion | It is not flammable in any general application but flammable in powder form |
| Chemical Reactivity | It is highly reactive to other elements |
| Valency of Element | +3 |
Different States of Aluminium
Chemically speaking, aluminum is a post-transition metal, which forms compounds in the +3 oxidation state. At room temperature, aluminium is solid, which means that it has the ability to hold its own shape and volume. Its total volume doesn’t change even if you bend and tear it.
What are the common uses of aluminum?
Aluminium is resistant to corrosion, low in density, and low in cost, which are the main reasons why it is used in various applications.
Food packaging and cooking pots
- Aluminium has no aroma, which explains why it is primarily used in making cooking pots and food packaging.
Electrical conductor
- Aluminium is a good electrical conductor, although not that good when compared to copper and silver. It can be used in overhead power lines because it is lighter and cheaper.
Used in a wide array of products
- Many products on the market today have aluminium in them, such as drinking cans, window frames, aircraft, and boats.
High-rise buildings
- Aluminium is one of the essential materials used in high-rise buildings and skyscrapers. It is because of aluminum’s durability, high strength-to-weight ratio, malleability, design flexibility, and versatility.
Consumer electronics
- Aluminium is one of the primary materials used in creating consumer electronics such as flat-screen TVs, laptops, tablets, smartphones, and computer monitors.
Household and industrial appliances
- Aluminium is used in air conditioning units and refrigerators, specifically in the precision tubing.
Component of spacecraft
- Aluminium alloy is now used in the making of spacecraft and rocket technology.
Ships
- The lightweight property of aluminium makes it a perfect component for making ships. It allows more surface and less mass, but most of all, it is strong enough to withstand cracks.
Personal vehicles
- One of the good things about aluminium is that it is environment-friendly and cost-effective. When used in vehicles, it can boost fuel economy, increase performance, and reduce smoke emissions. It does improve the safety and durability of vehicles.
Price of Aluminum
Pure aluminium cost around $15.72 per 100 grams. You can save money if you purchase in bulk. However, the price fluctuates depending on the supply and demand.
Interesting facts about Aluminium
- Don’t you know that it takes a lot of energy to manufacture aluminum? To produce one metric ton of aluminum, it would require 17.4 megawatt hours of electrical energy.
- Aluminium is a recyclable metal. It uses only 5% energy to recycle aluminum.
- The earth’s crust has a high level of aluminum, way higher than other metals.
- Don’t you know that although aluminum is metal, it does not stick to magnets under normal conditions?
- Don’t you know that there was a time when aluminum was more valuable than gold? It was in the 1850s when it is priced at $1,200 per kilogram.
- Don’t you know that the gemstone ruby is primarily made from aluminum oxide? Aluminium ions were replaced by chromium ions.
Pictures of Aluminium


Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What chemical element does aluminum react with?
Aluminium is reactive to halogens and form aluminium halides, specifically reactive to bromine, chlorine, and iodine to form aluminium iodide, aluminium bromide, and aluminium chloride.
Q2. Does aluminium possess danger to humans?
Aluminium is not dangerous to humans, but if you are exposed to an extremely high level of aluminium, it can be potentially dangerous to your health. it could increase the possibility of lung-related diseases such as cough and abnormal results in chest x-rays.
Q3. Does aluminium have negative impact to your brain?
Aluminum has a negative impact on the brain. It can contribute to a wide array of neurodegenerative diseases such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and Alzheimer’s disease. If you have been exposed to a severely high level of aluminum, there is a need for therapy or treatment to bring down the ill effects of aluminium in the body.
Q4. What chemicals should not be stored together with aluminum?
When storing aluminum, one thing you should keep in mind is to not store it with strong acids like nitric sulfuric, and hydrochloric acid. You should not also store it together with oxidizing agents like nitrates, fluorine, chlorine, and bromine. Aluminium should not also be stored together with strong bases and chlorinated hydrocarbons.
Q5. What is corrosive to aluminum?
Heavy metals can cause deposition corrosion of aluminium. It includes mercury, copper, nickel, lead, and tin. Corrosion is more pronounce in acidic solutions than alkaline solutions.
References
- https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/13/aluminium
- https://www.britannica.com/science/aluminum
- https://www.livescience.com/28865-aluminum.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aluminium
- https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/al.htm
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Aluminum
- https://www.chemicool.com/elements/aluminum.html
- https://www.aluminiumleader.com/about_aluminium/what_is_aluminum/
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/aluminum-definition-properties-uses.html
- https://www.thoughtco.com/aluminum-or-aluminium-facts-606496