What is Cobalt?
Cobalt is a hard, lustrous, and brittle chemical element characterized as hard ferromagnetic. It shares the same characteristics as nickel and iron. Cobalt itself is active and forms various compounds. In the air, it remains stable, but can be affected by dilute acids.
Where is Cobalt obtained?
The source of cobalt is the mineral cobaltite, erythrite, and skutterudite. The ore deposits used to obtain cobalt are found in Brazil, Zambia, Australia, Canada, and DR Congo. The majority of cobalt is formed as a byproduct of refining nickel, lead, silver, copper, and iron. It is important to note that cobalt does not exist as a free element. It is present in the crust of the earth.

History of Cobalt
Cobalt was discovered in 1735 by a Swedish chemist by the name of George Brandt. He was able to successfully discover cobalt by isolating it and proved that it’s the one responsible for giving blue glass color, which was thought to be caused by bismuth.
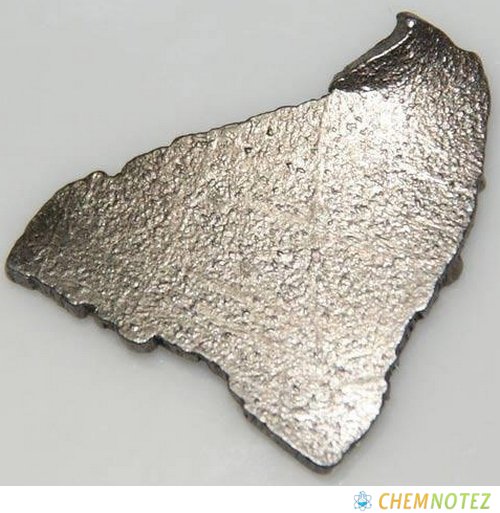

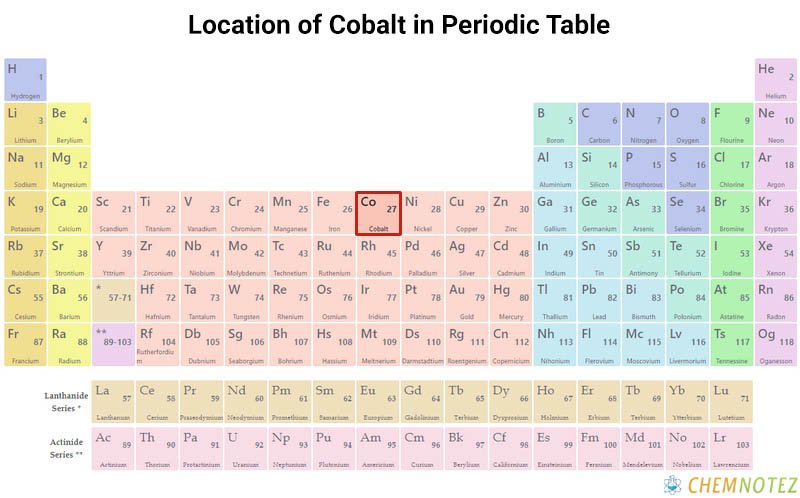
Classification, Properties, and Characteristics of Cobalt
Cobalt is a hard metal at room temperature. However, it is also brittle. It is characterized by bluish-white color. It is naturally magnetic, can be magnetized easily, and has the ability to maintain its ability to magnetize even at high temperatures. It is also somewhat reactive. When exposed to oxygen in the air, it gets slowly reactive. It also has the ability to form various compounds when combined with other elements.
Lewis Dot Structure of Cobalt

Bohr’s Atomic Model of Cobalt

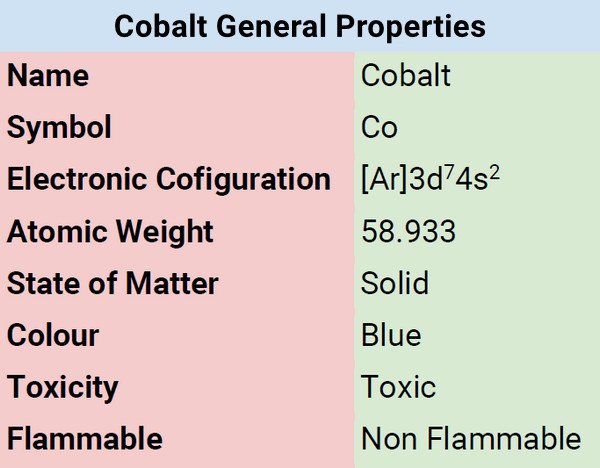
Atomic Data of Cobalt
Physical Properties of Cobalt
| Color | Silvery blue/silvery white |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Tasteless |
| Atomic Mass | 58.933 |
| Weight | 58.933194 |
| Density | 8.9 gram/cm3 at 20 °C (68 °F) |
| Atomic Radius | 2.00 Å |
| Ionization Energy | 760.402 kJ mol−1 |
| Covalent Radius | 1.18 Å |
| Ionic Radius | 0.078 nm (+2) ; 0.063 nm (+3) |
| Electronic Gain Enthalpy | 63.7 kJ/mol |
| Electron Negativity | 1.88 |
| Electron Affinity | 63.873 kJ mol−1 |
| Melting Point | 1,495 °C (2,723 °F) |
| Boiling Point | 2,870 °C (5,198 °F) |
Chemical Properties of Cobalt
| Atomic Number | 27 |
| Group | 9 |
| Period | 4 |
| Block | d |
| Electronic Configuration | [Ar]3d74s2 |
| Combustion | Not combustible in solid form |
| Chemical Reactivity | Somewhat reactive |
| Valency of Element | 3, 2 |
Different States of Cobalt
Cobalt is solid at room temperature. It exists with oxidation states that could range from -3 to +4, +2 and +3 are the most common oxidation states.

Uses of Cobalt
- It is primarily used to make magnets. It can turn into powerful magnets by alloying it with nickel and aluminum.
- Cobalt alloys are used in industries that use high-temperature strength such as gas turbine generators and jet turbines.
- Cobalt metals play an important role in electroplating because of their attractive physical appearance. It is also hard and has the ability to resist corrosion.
- Cobalt has medical significance too. Cobalt-60 is used to treat some types of cancer.
- Radioactive cobalt-60 is used to preserve food.
- Cobalt salts are used to create a bright blue color in pottery products, enamels, porcelain, paint, cosmetics, and glass.
- In the body, cobalt is a vital trace element and serves as an active site for the B12 vitamin. The body only needs a small amount of cobalt.
- Mineral deficiencies in animals are corrected using a small dose of cobalt salts.
- Cobalt is used to create superalloys because of its ability to resist corrosion and remains stale despite extremely high temperatures.
- Cobalt is used to make batteries.
- Cobalt is one of the components used in making samarium-cobalt permanent magnets, which are used for making high-speed motors and guitar pickups.
Price of Cobalt
The cost of cobalt is dependent on supply and demand. Pure cobalt costs around $21 per 100 grams. For bulk orders, the cost is lower, which is usually around $4.40 per 100 grams.
Interesting facts about Cobalt
- Don’t you know that cobalt was the first metal to be discovered and the first ever metal to be known with a discovery?
- Don’t you know that an imbalance of cobalt, meaning too much or too little can have a detrimental effect on the body?
- Cobalt has agricultural significance. A small amount of cobalt is used as a fertilizer.
- The majority of cobalt in the United States came from other countries.
- Don’t you know cobalt came from German miners? It was named after Kobalds.
- The bright blue color of cobalt was attributed to bismuth. One of the components of cobalt is bismuth and many don’t believe it until it was proved by a Swedish chemist, Georg Brandt.
- A strong source of gamma radiation is isotope Co-60.
- Don’t you know that cobalt is the main atom in the B12 vitamins?
- Don’t you know that cobalt is ferromagnetic, which means that it has the ability to retain its magnetic characteristic even at extremely high temperatures?
- Cobalt has a total of six oxidation states, but the most common of these six are +2 and +3.
- The estimated amount of cobalt in seawater is 2 x 10-5 mg/L.
- Don’t you know that Egypt has the oldest cobalt-colored glass? It was discovered in 1550-1292 B. C.
- The estimated amount of cobalt in the earth’s crust is around 25 mg/kg.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Is there a substance that cobalt doesn’t react with?
Cobalt is reactive to acids and produces hydrogen gas. If there is one substance that cobalt does not react with, it would be water. However, it is only not reactive to water at room temperature.
Q2. Is cobalt safe in the water?
The presence of cobalt in water does not possess any danger to humans and animals. However, it is not harmful when it is in non-radioactive form.
Q3. Does cobalt burn skin?
Cobalt undergoes decay process by gamma radiation. If you are exposed to a large amount of Cobalt 60, there is a possibility of skin burns. In fact, the effect goes beyond the burning of the skin. It can cause acute radiation sickness. If not dealt with right away, it could lead to death.
Q4. Can cobalt be destroyed?
Unfortunately, it cannot be destroyed. Cobalt has the ability to change its form. It can also attach to or separate itself from other particles. Radioactive decay pertains to the process of decreasing the level of radioactive cobalt in the environment.
Q5. How much cobalt is in the human body?
The level of cobalt in the adult human body is around 1 mg. About 85% of cobalt in the body is in vitamin B12 form. The human body needs between 5 and 50 μg/day. The majority of cobalt taken by humans is in inorganic form.
References
- https://www.britannica.com/science/cobalt-chemical-element
- https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/27/cobalt
- https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/co.htm
- https://www.livescience.com/29275-cobalt.html
- https://www.ducksters.com/science/chemistry/cobalt.php
- https://www.chemicool.com/elements/cobalt.html
- https://www.thoughtco.com/cobalt-element-facts-606520
- https://study.com/learn/lesson/cobalt-co-element-facts-properties-uses.html
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Cobalt
- https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele027.html