What is helium?
Helium is an inert gas (a noble gas) and the second lightest chemical element. It is an odorless, colorless, and tasteless gas but transforms into liquid at the right temperature. One thing to know about helium is that it is the only chemical element that does not solidify even with sufficient cooling and suitable atmospheric pressure.

Where Helium is obtained?
The majority of helium is a radioactive decay product of thorium and uranium. There is abundant helium in the earth’s crust. The majority of available helium today is the commercial type, and it is extracted from natural gas. The majority of helium reserves are in the United States (Texas and Kansas), Algeria, and Qatar. There is also helium beneath Tanzania, but it’s still a recent discovery and would require in-depth scientific study.
History of Helium
How was helium discovered? It was through the efforts of an astronomer, Pierre Janssen. He was able to detect a bright yellow line in the gaseous atmosphere surrounding the sun, specifically during the 1868 eclipse. During that time, it was assumed that the line was sodium.
Another person by the name of Joseph Norman Lockyer, an English astronomer, observed the appearance of a yellow line in the solar spectrum and that particular line isn’t the same as the sodium’s D1 and D2 lines. Thus, he named that line the D3 line.
He eventually thought that the D3 line is a result of an element in the sun. Lockyer and another chemist, Edward Frankland, used the Greek word hēlios, which means “sun,” in naming the element.
In 1985, Sir William Ramsay, a British chemist, discovered the presence of helium on Earth. He got a cleveite (a uranium-bearing mineral) sample.They heated a sample and examined the gas it produced, and found the presence of a bright yellow line in the spectrum that matches the D3 line in the sun’s spectrum.
Eventually, in 1903, Frederick Soddy and Sir William Ramsay found out that helium is a result of a continuous disintegration of radioactive materials. The formal discovery of helium was made through the efforts of Per Teodor Cleve and Nils Abraham when they found out that helium came from uranium ore.
Classification, Properties and Characteristics of Helium
Helium is an inert monatomic gas that is light, colorless, and odorless. It has the ability to form diatomic molecules, but a weak one. It has the lowest melting point and the boiling point is close to absolute zero. It does not solidify. It remains liquid even at absolute zero temperatures under ordinary pressures.
As a non-toxic gas, helium is less soluble in water, less reactive, and does not form chemical compounds. It also has a very low density and viscosity. However, its caloric content and thermic conductivity are extremely high. It can be liquified, but has the lowest condensation temperature when compared with other substances.
The Lewis Dot Structure of Helium
Helium is denoted by the symbol He. Unlike other noble gases of the same group, helium only has two valence electrons. It is represented by two lone pairs of dots in the Lewis symbol – He:

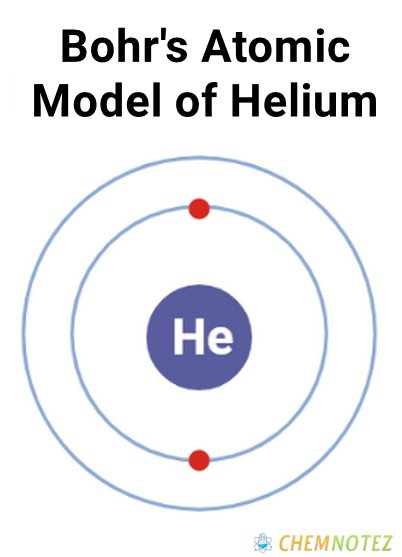
Bohr’s Atomic model of Helium
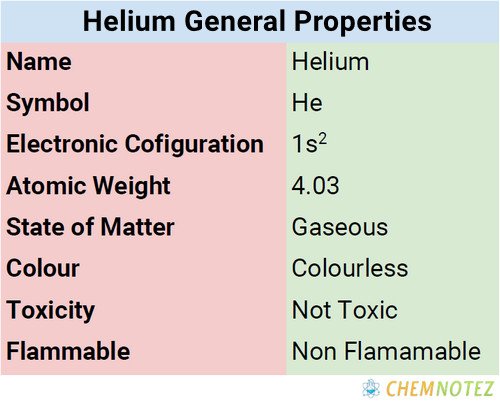
Physical Properties of Helium
| color | silvery white/light silver-gray |
| odor | odorless |
| Taste | sweet |
| Atomic mass | 4.003 |
| Weight | 4.002602 |
| Density | 0.1785 gram/litre |
| Atomic Radius | 140 pm |
| Covalent Radius | 28 pm |
| Ionic Radius | 93 |
| Ionization Energy | 24.5874 eV |
| Electronic Gain Enthalapy | 48 |
| Electron Negativity | None |
| Electron Affinity | -0.5(2) |
| Melting Point | -272.2 °C |
| Boiling Point | −268.9 °C (−452 °F) |
Chemical Properties of Helium
| Atomic Number | 4 |
| Group | 2 Alkaline Earth Metal |
| Period | 2 |
| Block | s |
| Electronic configuration | [He]2s2 |
| Combustion | Combustible/will ignite if the surrounding is in fire |
| Chemical Reactivity | Relatively unreactive at room temperature |
| Valency of Element | +2 |
Different States of Helium
Liquid Forms

- Helium has two liquid forms, namely Helium I and Helium II.
- Helium I – It is the normal liquid form of helium and exists at temperatures from its boiling point of 4.21 K to 21.8 K.
- Helium II – If the temperature goes below 21.8 k, helium’s thermal conductivity becomes greater than copper by a thousand times. During this phase, helium is viscous, superfluid, and resistant to flow.
Gas
Helium in a gas state is the second least reactive of all chemical elements. It has a relatively low atomic mass. It also has greater specific heat, thermal conductivity, and sound speed than all other gaseous elements except hydrogen.
Common uses of Helium
Helium has many uses across various industries. These are the following:

- Helium is used for welding metals. It is used for inert-gas atmospheres, especially when welding aluminum.
- Helium is used for rocket propulsion, specifically to pressurize fuel tanks.
- Helium is used as a lifting gas for equipment-carrying balloons.
- Helium is useful in the medical field because it acts as an effective cooling medium for LHC, especially in cryogenics. It also serves as a superconducting magnet in NMR spectrometers and MRI scanners.
- Helium is used in high-pressure breathing operations, such as in the case of scuba diving, where helium is mixed with oxygen.
- Helium is used to fill decorative balloons and airships.
- Helium is effective in keeping satellite instruments cool. In fact, it was used to cool liquid oxygen that powered space vehicles like the Apollo.
- The unreactive nature of helium makes it suitable for use as an inert protective atmosphere for creating semiconductors and fibre options.
- Detecting leaks is also possible with the help of helium, especially in detecting leaks in car air-conditioning systems.
- There are now supermarkets that use helium-neon gas lasers, specifically for scanning barcodes in supermarket checkouts.
- In the laboratory, the helium-ion microscope replaces the scanning electron microscope as the former gives better image resolution.
Price of Helium
The market price of helium fluctuates depending on demand and source. The current market value of helium is $7.21 per normal cubic meter.
Interesting facts about helium
- Helium is so extremely low in density that it floats in the air.
- When helium is inhaled, it creates a weird squeaky voice, and it is because of helium’s low density.
- Too much inhalation of helium can be fatal as it can replace oxygen in the lungs.
- Helium is the second most abundant chemical element in the universe.
- Helium can escape the earth’s gravity because its atoms are extremely light.
- The Sun produces around 700 million tons of helium per second.
- Helium is the very first chemical element that was not discovered on Earth.
- When a helium atom fuses, it forms oxygen, silicon, and carbon.
Frequently Asked Questions about Helium
Q1. Is there a shortage in the earth’s supply of helium?
Although helium is common in the solar system, it is ironic that it is rare on Earth. The reason for this is that once helium escapes the earth’s atmosphere, it disappears into space because its atoms are so light that the earth’s gravity cannot trap them.
Q2. What makes helium special?
Helium is one of the special chemical elements because of its rare and unique characteristics. It is an inert gas, which means that it does not react chemically. It is lighter than the air and has the lowest melting point among all monatomic gases, which makes it useful in various industries such as cryogenics and supercooling.
Q3. What’s the reason behind helium’s low melting point?
Helium has a low melting point primarily because of little interaction between the noble gas atoms. As the element’s atomic size increases, so do the inter-molecular forces.
Q4. Can helium be used in medicine?
Yes, helium is useful in the medical field. In fact, it can be used for the treatment of respiratory conditions such as emphysema and asthma. Helium in liquid form is used in various medical equipment and tools such as in MRI scanners and NMR spectrometers wherein helium is used as a cooling medium for magnets.
Q5. Is there a potential danger in using helium?
Helium can be potentially dangerous when inhaled. Unlike the usual air, helium possess danger because once inhaled in the body, it can cause the body’s oxygen level to drop to an extremely low level causing hypoxia also known as inert gas asphyxiation.
References
- https://www.britannica.com/science/helium-chemical-element
- https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/2/helium
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Helium
- https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/he.htm
- https://byjus.com/chemistry/helium/
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Helium
- https://www.sciencelearn.org.nz/resources/2759-helium
- https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele002.html
- http://www.chemistryexplained.com/elements/C-K/Helium.html
- https://www.priyamstudycentre.com/2020/11/helium.html