What is Lithium?
Lithium is a soft metal, silvery and lustrous in nature, and has the lowest density of all elements in the metal group. It is reactive with water. In the periodic table of elements, lithium is the first of the alkalis. The majority of its chemical and physical properties are the same as those of alkaline earth metals.

Where is Lithium obtained?
The reactive nature of lithium makes it difficult to find in nature in its pure form. Although it is abundant in various parts of the world, such as mineral springs, seawater, and igneous rocks, Seawater has lithium chloride, but it needs to be extracted in lithium carbonate form.
It will be re-treated to separate ions and reduce them, such as in the process of lithium ores. In the world, there are only three seawater lakes where lithium is extracted, and these are Argentina, Chile, and Nevada.
History of Lithium
Lithium was discovered in a mineral, which explains the name; Green’s work “lithos,” which means “stone.”It was Jozé Bonifácio de Andralda e Silva, who discovered the very first lithium mineral, petalite, in 1790 on the Swedish Island of Utö.
When that particular mineral is thrown onto a fire, it causes an intense crimson flame. Johan August Arfvedson analyzed the mineral and found out that it contained an unknown metal, which he eventually referred to as lithium.
Arfvedson later discovered that the metal is alkali and much lighter than sodium.The only distinguishing factor between lithium and sodium is that the former cannot be separated by electrolysis.
In 1855, Augustus Matthiessen (British chemist) and Robert Bunsen (German chemist) subjected molten lithium chloride to electrolysis and were eventually able to obtain bulk lithium.
Classification, Properties, and Characteristics
Lithium’s characteristics and properties are the same as those of the alkali metal groups such as potassium and sodium. Lithium is highly reactive with water. It floats in water and forms a robust hydroxide solution, leading to the formation of hydrogen gas and lithium hydroxide. If lithium and its compounds are thrown into the flame, they display a crimson color.
One particular characteristic of lithium is its corrosive nature, and it requires knowledge and expertise to handle it well. Lithium in its elemental form is highly flammable. So, you have to be cautious when handling lithium.
Lewis Dot Structure of Lithium
Lithium belongs to the 1A group, and each atom has one valence electron. Lithium’s electron diagram is similar to that of hydrogen. Hence, the Lewis Dot Structure of Lithium is •Li.

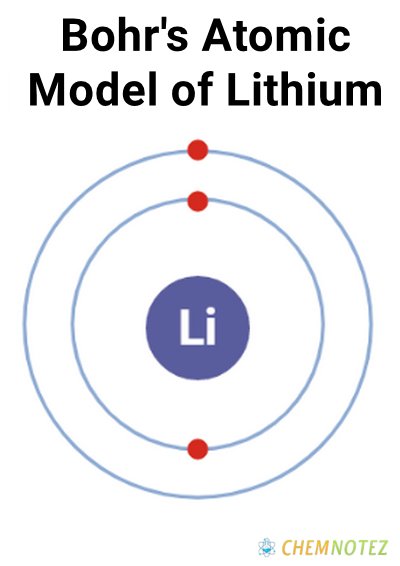
Bohr’s Atomic Model of Lithium
Physical Properties of Lithium
| Color | silvery white |
| Odor | Oderless |
| Taste | acid Taste (Strong Metallic taste ) |
| Atomic mass | 6.941 u |
| Weight | 1.00794 |
| Density | 0.08988 g/L |
| Atomic Radius | 53 pm |
| Ionization Energy | 5.4 eV |
| Ionic radius | 182 pm |
| Covalent Radius | 128 pm |
| Electronic Gain Enthalapy | -60 |
| Electron Negativity | 0.98 |
| Electron Affinity | 59.6 kJ/mo |
| Melting Point | 180.50°C, 356.90°F, 453.65 K |
| Boiling Point | 1342°C, 2448°F, 1615 K |
Chemical Properties of Lithium
| Atomic Number | 3 |
| Group | 1 |
| Period | 2 |
| Block | s |
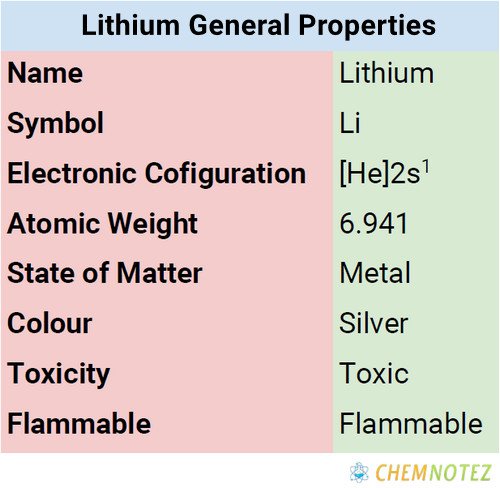
| Electronic Configuration | [He] 2s1 |
| Combustion | Highly Combustible |
| Chemical Reactivity | Reactive with other elements |
| Valency of Element | 1 |
Different States of Lithium
- At normal temperatures, lithium is a soft metal characterized by a silvery white color.
- Of all solid elements, lithium has the highest specific heat capacity.
- It is reactive to air and water, thus the need to store lithium in mineral oil.
- Lithium in crystalline form is silver-white and soft.
- When it is at solid room temperature, it is not as dangerous as it may seem, for it starts to evaporate when the temperature exceeds 600 ‘C.
- When molten lithium comes into contact with moist skin, it is so reactive and dangerous that it causes burns.
What are the most common applications for lithium?
Rechargeable and non-rechargeable batteries
- Lithium is used in rechargeable batteries for laptops, mobile phones, digital cameras, and electric cars.
- It also plays an important role in non-rechargeable batteries like toys, clocks, and heart pacemakers.

Creating metals
- Lithium metal is transformed into alloys in combination with magnesium and aluminium to make them lighter, but more durable.
- An alloy made from magnesium and lithium is used for armour plating.
- On the other hand, lithium and aluminum combinations are used in bicycle frames, high-speed trains, and aircraft.
Glass and glass ceramics
- Lithium oxide is used in creating glass wares and glass ceramics.
Industrial setting
- In industrial drying systems and air conditioning, lithium chloride, specifically lithium bromide, is used.
Lubricant
- Lithium stearate is used as a lubricant.
Medical purpose
- Lithium carbonate is used to treat certain types of medical conditions, such as in the management of manic depressive disorder.
Organic synthesis
- Lithium is useful in organic synthesis in industrial and laboratory settings.
Nuclear reactors
- Lithium plays an important role in nuclear reactors, making it an essential component for scientists in doing experiments. It is widely used in chemical reactions and processes.
Price of Lithium
The current price of lithium is US $0.0171. The figure fluctuates depending on the demand and other relevant factors.
Interesting facts about lithium
- Lithium is a metal, but it’s soft enough that it can be cut using a regular knife.
- Lithium is so light that it floats on water.
- Lithium gives off a bright red flame when burned, and it is commonly used in a flame test.
- Lithium is widely used in rechargeable batteries, although there are a few non-chargeable batteries that use lithium.
- Lithium fire is difficult to put out for the reason that it is reactive to water. If you use water to put out the fire, it will make the fire worse. You will need a powder fire extinguisher to put out lithium fire.
- Lithium is the only metal in the alkali group that is reactive with nitrogen.
- The light weight of lithium makes it perfect to be alloyed with other metals like copper and aluminum.
- Lithium hydroxide is used to purify air and get rid of carbon dioxide in submarines and spacecraft.
Images of Lithium



Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What makes lithium highly flammable?
Lithium, although it has plenty of uses, must be handled with utmost care as it is highly flammable. It reacts violently with water, steam, or moisture. Once it gets in contact with these things, it produces heat and flame. It can easily catch fire and burn tremendously. In rare instances, it can cause explosions.
Q2. Why is lithium fire difficult to put out?
A fire caused by lithium is very challenging to extinguish because of the nature of lithium, particularly its reactivity to water. Once lithium gets in contact with water, it produces hydrogen gas and lithium hydroxide. The former is highly flammable. Pouring water on the fire is counterproductive and can be extremely dangerous.
The same thing goes for lithium-ion batteries. Once it is exposed to moisture or air, it can cause hydrofluoric acid, a highly toxic substance that can cause irritation to the eyes and lungs.
Q3. What makes lithium unique?
Lithium is a special chemical element, particularly in the metal group, because of its soft and light characteristics. When we refer to metal, we picture it as something tough and durable, but lithium is an exemption.
It is a soft metal that can be cut using a kitchen knife. It does not submerge in water because it is extremely low in density. In fact, it is way too low that it floats on water.
Q4. What chemical elements work well with lithium?
At room temperature, lithium does not react with oxygen. However, it starts to react with oxygen if the room temperature exceeds 100 °C, forming lithium oxide. Lithium can also combine with other elements such as
References
- https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/3/lithium
- https://www.britannica.com/science/lithium-chemical-element
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lithium
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Lithium
- https://www.chemicool.com/elements/lithium.html
- https://www.livescience.com/28579-lithium.html
- https://www.nrcan.gc.ca/our-natural-resources/minerals-mining/minerals-metals-facts/lithium-facts/24009
- https://www.solvay.com/en/innovation/elements-periodic-table/lithium
- https://www.worldofmolecules.com/elements/lithium.htm
- http://www.chemistryexplained.com/elements/L-P/Lithium.html