What is Magnesium?
Magnesium belongs to the group 2a, with the symbol Mg. It is a strong yet lightweight metal known for its shiny silvery color. It is the lightest of all metallic elements. Magnesium and its compounds are commonly used in medicine and the construction industry. As a matter of fact, magnesium is one of the essential elements to all cellular life.

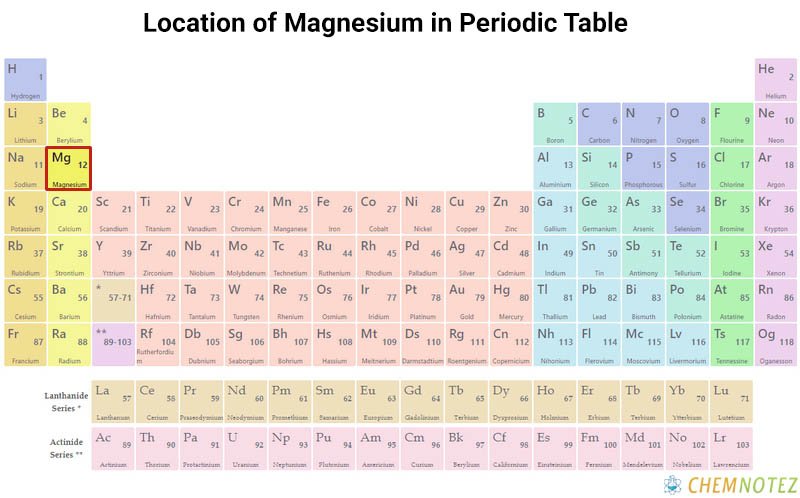
Where is Magnesium obtained?
Magnesium is found in minerals like magnesite and dolomite. The sea is where you can find a large deposit of magnesium, which is around trillions of tonnes. In fact, about 850,000 tonnes of magnesium produced every year come from the sea. To get magnesium, magnesium oxide is reduced with silicon. It could also be done by molten magnesium chloride electrolysis.

History of Magnesium
Many decades ago, people believed that magnesium and calcium were the same element. Nobody knew the difference between the two until 1755. Joseph Black, a Scottish chemist, conducted an experiment to find the difference between the two elements.
In 1808, Sir Humphrey Davy, successfully isolated magnesium using magnesium-mercury amalgam and eventually evaporating the element. How does he manage to do it? He used a large battery that conducts electricity through the salt (magnesium amalgam).
He created an amalgam by creating a paste out of moist red mercury oxide and magnesium oxide. He created a tiny well in the paste and put in mercury metal, which serves as a negative electrode. With the help of the battery, he introduced electricity to the paste to heat up the amalgam and separate elemental magnesium.
Classification, Properties and Characteristics of Magnesium
Magnesium is low in density, strong, and tarnishes in air, thus forming a thin coating of oxide. It is resistant to corrosion and can withstand high temperatures. It is reactive to water to produce hydrogen gas.
Lewis Dot Structure of magnesium

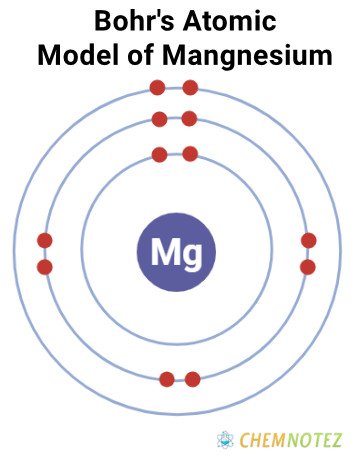
Bohr’s Atomic Model of Magnesium
Atomic Data of sodium
Physical Properties of magnesium
| Color | silvery white |
| Odor | odorless |
| Taste | sour, bitter, and salty taste |
| Atomic Mass | 24.305 |
| Weight | 24.305 |
| Density | 1.74 |
| Atomic Radius | 1.6 Å |
| Ionization Energy | 7.6462 eV |
| Covalent Radius | 1.41 Å |
| Ionic Radius | 173 pm |
| Electronic Gain Enthalpy | +230 kJ/mol |
| Electron Negativity | 1.31 |
| Electron Affinity | Not stable |
| Melting Point | 650°C, 1202°F, 923 K |
| Boiling Point | 1090°C, 1994°F, 1363 K |
Chemical Properties of magnesium
| Atomic Number | 12 |
| Group | 2 |
| Period | 3 |
| Block | s |
| Electronic Configuration | [Ne] 3s2 |
| Combustion | It is not a combustible metal |
| Chemical Reactivity | Magnesium compounds are highly reactive |
| Valency of Element | 2 |

Different states of magnesium
As an alkaline metal, magnesium is solid at room temperature. It keeps its solid state because of an extremely strong intermolecular force. It would take a lot of energy to transform magnesium from solid to liquid or gas.

What are the common uses of magnesium?
Use as an alloying agent
- Magnesium makes a very good alloying agent. It is less dense than aluminium, thus improves any work that includes aluminium, especially in terms of fabrication, mechanical, and welding. These materials can be found in the construction of automobiles and airplanes.
Use in lightweight products
- Magnesium is one of the components used in creating lightweight products like luggage, car seats, cameras, laptops, and power tools.
Removing sulfur
- Magnesium is added to steel and molten iron to get rid of sulfur.
Use in fireworks
- When magnesium gets in contact with the air, it ignites and burns, creating a bright light; thus, the very reason it is used in making fireworks, flares, and sparkles.
Dye mordant
- Magnesium and its compounds, such as magnesium sulfate, can be used as dye mordants.
Fire retardant
- Magnesium hydroxide makes a very good fire retardant, which is why it is being added to plastic materials.
Heat resistant
- Magnesium oxide is used to make objects resistant to heat. It is usually used in furnaces and fireplaces.
Medicinal purpose
- Magnesium compounds have medicinal purposes, such as magnesium sulfate, also known as Epsom salts, magnesium hydroxide, or milk of magnesia, magnesium citrate, and magnesium chloride.
- Magnesium is added to fertilizers and cattle feed.
Biological activities
- Magnesium plays a crucial role in some biological activities, especially in animals and plants. In plants, magnesium enables plants to capture sunlight, which is one of the essential components in photosynthesis.
- In humans, magnesium is a must for enzymes to work. About 250 to 350 mg of magnesium is needed by humans every single day.
- About 20 grams of magnesium are stored in the bones.
Price of magnesium
The current market price of pure magnesium is around $3 to $3/100 grams.
Interesting facts about magnesium
- Magnesium is ranked 8th in the list of the most abundant elements on earth.
- Magnesium oxide is abundant in the earth’s crust. In fact, it is the second most abundant element.
- A fire with magnesium in it is extremely difficult to put out. You cannot extinguish it using water.
- Don’t you know that of all the elements in the metallic group, magnesium is the lightest in terms of weight?
- Don’t you know that there are about 1.3 billion kg of magnesium in every cubic kilometer of seawater?
- Here’s another fun fact: magnesium is derived from the word “magnesia”, a region found in Greece.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Does magnesium burn in water?
Once magnesium gets in contact with water, it forms hydrogen gas. The excess oxygen and heat supply cause violent ignition. It will outrageously burn to decrease water molecules, turning them into hydrogen gas.
Q2. What element does magnesium react with?
Magnesium is highly reactive to oxygen. It forms magnesium oxide. It is also reactive to hydrogen, forming magnesium hydride. Another element magnesium instantly reacts with is nitrogen. It turns into magnesium nitride. Magnesium is also highly reactive to halogens.
Q3. Is magnesium flammable?
Yes, it is an explosive hazard, particularly magnesium metal and its alloys. It is highly combustible in pure, molten, powder, or ribbon form. It does react violently to water.
Q4. Is magnesium toxic?
Fortunately, the kidneys can eliminate excess amount of magnesium through urination. If you eat foods with high magnesium, don’t worry as it will not possess any health risk. However, the only downside is that if you had too much magnesium such as in people under medication containing high level of magnesium, you might experience bouts of diarrhea with abdominal cramping and nausea. It could also be the case in people taking a high level of magnesium supplement.
Q5. What causes magnesium to burn?
If magnesium gets in contact with oxygen, it creates light bright that could cause temporary blindness. It burns so bright because of the release of heat.
References
- https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/12/magnesium
- https://www.britannica.com/science/magnesium
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Magnesium
- https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/mg.htm
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Magnesium
- https://www.chemicool.com/elements/magnesium.html
- https://chemistrytalk.org/magnesium-element/
- https://www.livescience.com/28862-magnesium.html
- https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele012.html
- https://www.thoughtco.com/magnesium-facts-606556