What is Molybdenum?
Molybdenum belongs to the metal group, is silvery-white in color, and has the ability to resist corrosion. Of all pure elements, Molybdenum is one that has the highest melting point. It is also considered a micronutrient making it essential for life. when drawn on paper, molybdenum makes a mark, which is typical to that of graphite and lead, thus, the reason why it was mistaken by scientists for over two decades. You’ll get to know more about molybdenum in this article.
Where is Molybdenum obtained?
There are seven mines producing molybdenum, but among those seven, only two produce pure molybdenum. These are Climax Mine in Colorado, which is owned by Freeport-McMoRan, and Kennecott Mine owned by Rio Tinto. Other molybdenum mining areas include China, Peru, and Chile. Some molybdenum is produced as a byproduct of copper and tungsten production.
History of Molybdenum
Molybdenite, by the look of it, looks like graphite. Many believed that it is a lead ore, but in 1778, Carl Scheele deeply analyzed the said ore and revealed that it was not graphite or lead. Some believed that it contains a new element, but at that time, it was difficult to reduce it to metal.
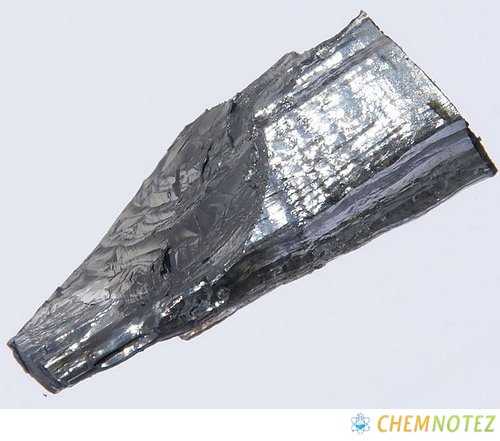

It can, however, be converted into oxide, and when water is added to it, it forms acid, which is now called molybdic acid. However, they failed to distinguish the said metal. Peter Jacob Hjelm, formed a paste by grounding molybdic acid and carbon together in linseed oil. He subjected it to red heat and was able to produce molybdenum metal. It was in 1781 when the new element was introduced formally.
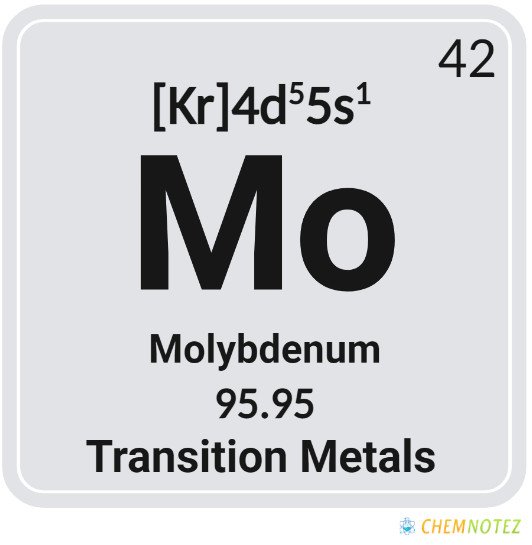
Classification, Properties, and Characteristics of Molybdenum
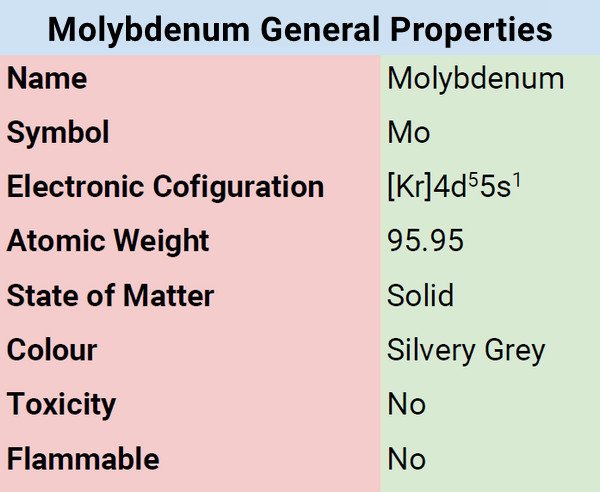
Molybdenum is a metal characterized by silvery-white color. It has a high melting point, thus, the reason why it is included in the list of five primary refractory metals. At room temperature, it is not reactive to water or oxygen and can resist corrosion. When in compound form, molybdenum usually has an oxidation state of IV and VI.
Lewis Dot Structure of Molybdenum

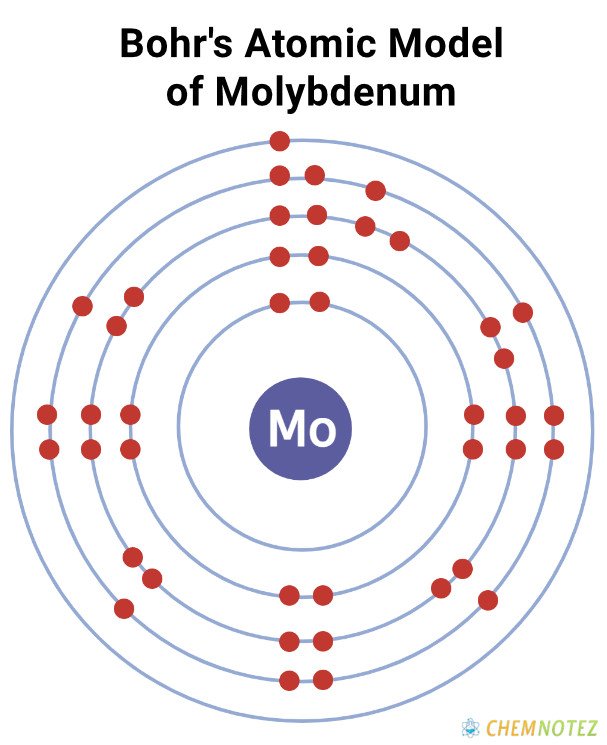
Bohr’s Atomic Model of Molybdenum
Atomic Data of Molybdenum
Physical Properties of Molybdenum
| Color | Silvery White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Tasteless |
| Atomic Mass | 95.94 g.mol -1 |
| Weight | 95.95 |
| Density | 10.2 g.cm-3 at 20°C |
| Atomic Radius | 2.17 Å |
| Ionization Energy | 684.316 kJ mol−1 |
| Covalent Radius | 1.46Å |
| Ionic Radius | 0.068 nm (+4) ; 0.06 nm (+6) |
| Electronic Gain Enthalpy | 72.171 kJ mol−1 |
| Electron Negativity | 1.8 |
| Electron Affinity | 72.171 kJ mol−1 |
| Melting Point | 2610 °C |
| Boiling Point | 4825 °C |
Chemical Properties of Molybdenum
| Atomic Number | 42 |
| Group | 6 |
| Period | 5 |
| Block | d |
| Electronic Configuration | [Kr]4d55s1 |
| Combustion | Flammable in powder and dust form |
| Chemical Reactivity | Reactive at high temperature |
| Valency of Element | 2,3,4,5 or 6 in different compounds |
Different States of Molybdenum
Molybdenum is solid at room temperature. To liquify it, it will require a very high temperature, a typical characteristic of elements that belong to the refractory metal group. It has various oxidation states with +4 and +6 as the most stable state.
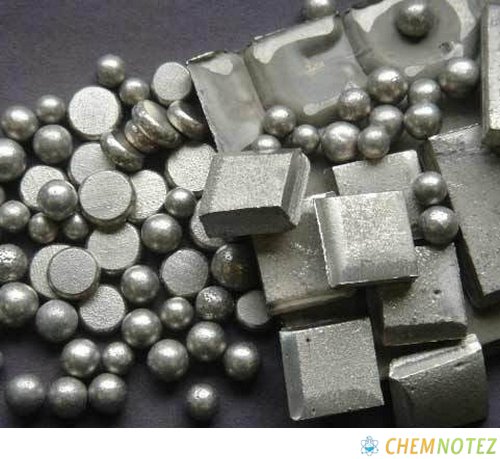

Uses of Molybdenum
- It functions as a valuable alloying agent. It adds strength and toughness to tempered and quenched steels.
- Molybdenum is used in some nickel-based alloys because of its ability to resist heat and corrosion.
- It is used as electrodes for glass furnaces powered by electricity.
- It is used in nuclear energy applications for aircraft and missile parts.
- It plays an important role in refining petroleum.
- A molybdenum compound, molybdenum sulfide functions as a lubricant, especially at high temperatures where there is a possibility of oil decomposition.
- Molybdenum in powder form is used in circuit links for circuit boards.
- Heat sinks and microwaves also use molybdenum.
- Molybdenum is one of the components of equipment exposed to extreme heat including saw blades and drills.
- It is useful in the petroleum sector. It acts as a catalyst allowing the removal of organic sulfur compounds in gas liquefaction and coal liquefaction methods.
- It acts as an integral component of the nitrogenase enzyme enabling the conversion of nitrogen gas in air into nitrates, which is essential for plant growth.
- You can find a trace amount of molybdenum in plants and animals. It is present in about 20 enzymes necessary in animal metabolism.
- It acts as a catalyst for plastic and polymer production by enabling proper selective oxidation through acrolein synthesis.
Price of Molybdenum
The cost of molybdenum varies depending on the supply and demand. Pure molybdenum costs around $44 per 100 grams. You will be able to save money if you purchase in bulk.
Interesting facts about Molybdenum
- Don’t you know that molybdenum comes from molybdenite minerals? It was originally thought to be graphite or lead but took years to eventually revealed the new element.
- Molybdenum comes from molybdos, a Greek word for lead-like.
- The mineral that contains the highest level of molybdenum is molybdenite.
- Don’t you know that in the 14th century, a specialized Japanese sword has molybdenum? The element was used as an alloying agent.
- Don’t you know that around 200,000 tons of molybdenum are produced every year worldwide?
- The largest molybdenum miners are in the United States of America, Peru, Chile, and China.
- A space program in Russia, Luna 24, was able to discover samples of molybdenum on the moon.
- Molybdenum ranked 54th in the list of most common elements found on earth’s crust.
- Molybdenum ranked 25th in the list of most common elements found in the earth’s oceans.
- It has a total of 35 known isotopes and seven of which occur naturally.
- Molybdenum is 6th on the list of elements with the highest melting point.
- Don’t you know that molybdenum has been useful in the military? Molybdenum was used as a plating on British WWI tanks, and as an alloyed steel used by the German army to create artillery pieces. German’s famous Big Bertha howitzers were made from steel alloy containing molybdenum.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What substances does molybdenum react with?
The reactivity of molybdenum is activated at high temperatures. At room temperature, molybdenum reacts with fluorine. Molybdenum slightly dissolves in hydrochloric, hydrofluoric, and sulfuric acid.
Q2. Why is the significance of molybdenum in living things?
Molybdenum is a vital trace element for all forms of life. it acts as a cofactor for a wide array of enzymes that catalyze essential chemical transformations in nitrogen, global carbon, and sulfur cycles.
Q3. Can you live without molybdenum?
One fact is that life cannot be sustained without molybdenum. Thus, the reason why molybdenum is found in small concentrations in living things such as animals, plants, and humans. It exists with a handful of other elements vital to life such as zinc, iron, and copper.
Q4. Is molybdenum resistant to acid?
Molybdenum can withstand many types of acids such as hydrofluoric acid, hydrochloric acid, and sulfuric acid. In fact, it is also resistant to many organic acids and molten materials like alloys glasses, and metals. However, in the presence of alkalis or oxidants, there is a possibility of molten corroding.
Q5. Is molybdenum toxic to the skin?
Molybdenum dust, when gets in contact with the skin, can cause irritation. It is also toxic when ingested or inhaled – usually causes gout-like signs and symptoms.
References
- https://www.livescience.com/34687-molybdenum.html
- https://www.britannica.com/science/molybdenum
- https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/mo.htm
- https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/42/molybdenum
- https://www.chemicool.com/elements/molybdenum.html
- https://www.refractorymetal.org/facts-about-molybdenum/
- https://www.thoughtco.com/molybdenum-facts-606561
- https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/Community/educationalresources/PeriodicTable/Molybdenum/
- https://study.com/learn/lesson/molybdenum-facts-uses-benefits.html
- https://chemistrytalk.org/molybdenum-element/