What is Niobium?
Niobium is an element that belongs to the metal group. It is shiny white that when exposed to air forms a film on the surface and when exposed to air, turns its color from shiny white to yellow, blue, or green. It has pretty interesting properties and characteristics. You will know more about niobium in this article.
Where is Niobium obtained?
The primary source of niobium is columbite, which also contains tantalum. The mineral columbite is abundant in Australia, Brazil, Canada, ad Nigeria. Niobium is also produced as a byproduct of extracting tin.

History of Niobium
Charles Hatchett examined minerals in a British Museum in 1801. He noticed a specimen labeled columbite and thought that it has a new metal in it, and turned out he was right. The next thing he did was heated the sample with potassium carbonate.

He dissolved it in water and added acid. He was able to get a precipitate from it. he was dismayed that he didn’t produce the element, but he named it columbium. Years went by and more people are keen to know more about the said element.
They began to doubt the existence of columbium, especially after the tantalum discovery as these metals exist together in nature. Heinrich Rose, a German chemist, proved in 1844 that columbite did has both elements and renamed the element from columbium to niobium.
Classification, Properties, and Characteristics of Niobium
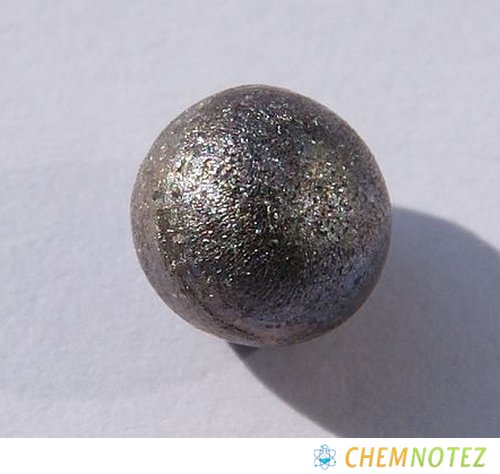
Niobium is characterized by its white shiny color. It is a ductile metal, but when exposed to air will begin to oxidize and turn into other colors such as green, blue, and yellow. The color will depend on its thickness. It has an oxide film that protects it from corrosion, but once it reaches a certain degree of temperature, it will start to oxidize.
It shares the same characteristics and properties as major refractory metals like tantalum, tungsten, rhenium, and molybdenum.
Lewis Dot Structure of Niobium

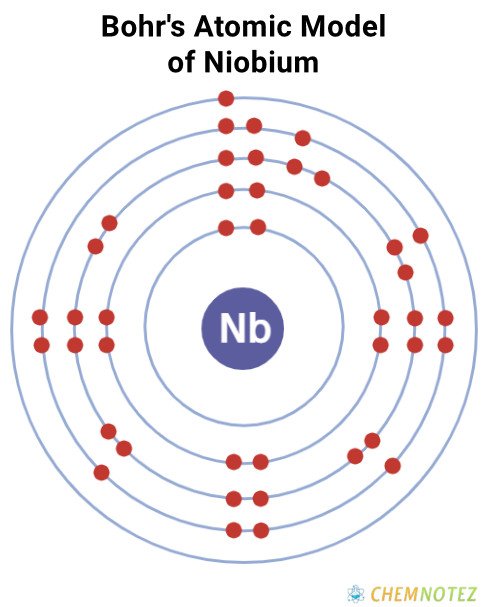
Bohr’s Atomic Model of Niobium
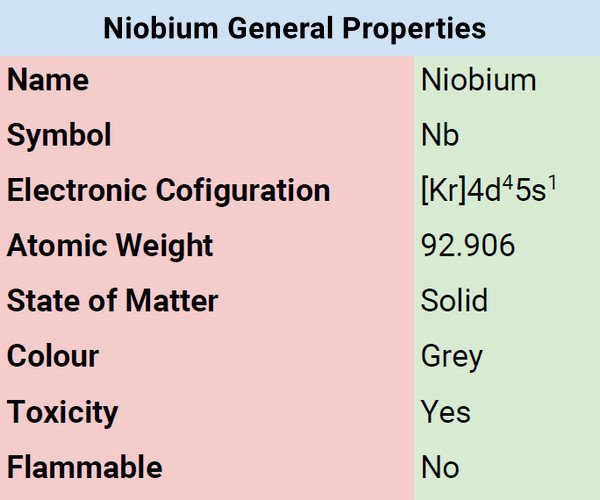
Atomic Data of Niobium
Physical Properties of Niobium
| Color | Silver |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Tasteless |
| Atomic Mass | 92.906 |
| Weight | 92.91 g.mol -1 |
| Density | 8.57 |
| Atomic Radius | 2.18Å |
| Ionization Energy | 652.13kJ mol−1 |
| Covalent Radius | 1.56 Å |
| Ionic Radius | 0.070 nm (+5) ; 0.069 nm (+4) |
| Electronic Gain Enthalpy | 88.381kJ mol−1 |
| Electron Negativity | 1.6 |
| Electron Affinity | 88.381kJ mol−1 |
| Melting Point | 2477°C, 4491°F, 2750 K |
| Boiling Point | 4741°C, 8566°F, 5014 K |
Chemical Properties of Niobium
| Atomic Number | 41 |
| Group | 5 |
| Period | 5 |
| Block | d |
| Electronic Configuration | [Kr]4d45s1 |
| Combustion | Highly flammable in powder form |
| Chemical Reactivity | Reactive to some elements |
| Valency of Element | 5 |
Different States of Niobium
Niobium is a transition metal, which means that it is solid at room temperature. It will turn to liquid once the desired temperature is reached.
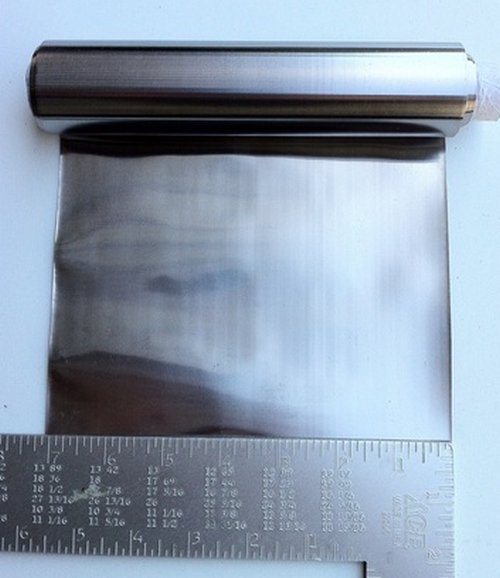


Uses of Niobium
- It is primarily used in alloys such as stainless steel because of its ability to improve alloy strength.
- Alloys that have niobium are used in special industries such as rockets, jet engines, girders and beams for buildings, gas and oil pipelines, and oil rigs. The reason why it is used in such heavy industry is not only because of its strength but also because of niobium’s ability to resist corrosion. It also resists distortion when exposed to high temperatures.
- Niobium is used in superconducting magnets for NMP equipment, MRI scanners, and particle accelerators because of its superconducting properties.
- Niobium oxide is added to glass products to improve their refractive index, thus the reason why corrective glasses now have thinner lenses.
- A particular niobium compound, niobium carbide is used in cutting equipment.
- Niobium alloys are in surgical implants because they are well-accepted by human tissues. So, there’s no possibility of the body rejecting the implant.
- Niobium is one of the materials used in making jewelry because it is hypoallergenic. Another thing that makes it suitable for jewelry craftsmanship is its ability to oxidize and promote anodizing, which is helpful in creating fine jewelry pieces like necklaces, chains, and jewelry used for body piercing such as nose studs, belly button rings, and hoops.
- Niobium is used in making lamp filaments.
Price of Niobium
The price of niobium is dependent on supply and demand. Pure niobium is priced at $18 per 100 grams.
Interesting facts about Niobium
- Don’t you know that for about 100 years, niobium was called columbium in the United States?
- Niobium has around 18 known isotopes.
- It is often mistaken for a rare earth metal.
- Brazil is the leading supplier of niobium in the world. About 90% of the world’s supply of niobium comes from Brazil. Next to Brazil is Quebec, Canada, which is the only operating underground niobium in the world.
- Around 80% of produced niobium in the world is used in the steel industry. It is used to manufacture ultra-strong steels.
- Niobium is one of the chemical elements named after Greek figures. It was named after Niobe, the Greek goddess of tears.
- An electric car battery developed by a well-known electronic company used a titanium-niobium oxide anode for lithium storage.
- Ferroniobium is one of the common niobium alloys, which is made in combination with iron.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Does niobium react with water?
Under normal conditions, niobium is not reactive with water primarily because its surface is protected by a thin layer of oxide.
Q2. Why is niobium expensive?
Niobium is considered a rare metal but can be found in various locations around the globe, especially in rocks of volcanic origin. Finding one can be extremely difficult, which explains why it is more expensive when compared to other elements.
Q3. What are the weaknesses of niobium?
Like any other metal, niobium has weaknesses too. it is inert to acids at room temperature, but can be attacked by hot concentrated acids. It can also be attacked by alkalis and oxidizing agents.
Q4. Is niobium safe to handle?
Yes. It is one of the safest chemical elements. In pure form, is it hypoallergenic and physiologically inert? It won’t cause any harmful reaction in the body.
Q5. Does niobium scratch easily?
Niobium is resistant to scratching, thus, one of the reasons why it is used to make jewelry pieces. It can be easily cut using a specialized jeweler’s saw. In fact, it can be forged and hand-formed easily.
References
- https://www.livescience.com/34682-niobium.html
- https://www.britannica.com/science/niobium
- https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/41/niobium
- https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/nb.htm#Environmental%20effects%20of%20niobium
- https://www.chemicool.com/elements/niobium.html
- https://study.com/learn/lesson/niobium-element-properties-uses-facts.html
- https://byjus.com/chemistry/niobium/
- https://sciencing.com/niobium-5031885.html
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Niobium
- https://www.chemistrylearner.com/niobium.html