What is Nitrogen?
Nitrogen is a chemical element classified as both non-metal and gas. It is tasteless, odorless, and colorless. It is important to life on earth because it serves many functions. In fact, it is present in all living systems. It is present in foods, organic materials, fertilizers, and even in poisons and explosives. Although nitrogen is important to life, it can be potentially dangerous in huge amounts. Nitrogen makes up 78% of the air on Earth.

Where is Nitrogen obtained?
A large reservoir of nitrogen is present in the atmosphere in the form of nitrogen gas. It enters the ecosystem through bacteria in the soil and plant roots. It converts nitrogen gas into ammonia through the process of nitrogen fixation.
Nitrogen can also be obtained from liquified air. The process is called fractional distillation. It is commercially produced to be used in ammonia production. A significant amount of nitrogen is mixed with hydrogen to create ammonia through the Haber process.
History of Nitrogen
A physician by the name of John Mayow in 1674 demonstrated that the air is not a sole entity. In fact, it consists of various substances and shows the combustible component of the air. After a century, Joseph Black, a Scottish chemist, conducted a detailed study of the air, but at that time only oxygen and carbon dioxide were removed.

Eventually, in 1772, Daniel Rutherford, a chemist and physician, removed carbon dioxide and oxygen from the air. He did an experiment using an empty bottle. He turned it over and trapped the air in it. He then lights up a candle in the bottle to use up oxygen, leaving behind the element nitrogen.
Classification, Properties and Characteristics of Nitrogen
Nitrogen is an inert gas at a normal temperature and pressure. It is tasteless, odorless, colorless, and diatomic. However, it is liquid at atmospheric pressure, especially at temperatures between 63 k and 77 k.

Lewis Dot Structure of Nitrogen

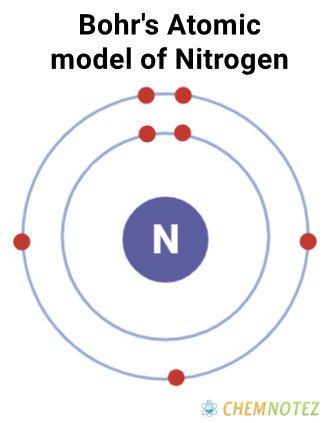
Bohr’s Atomic Model of Nitrogen
Atomic Data of Nitrogen
Physical Properties of Nitrogen
| Color | Colorless |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Tasteless |
| Atomic Mass | 14.007 |
| Weight | 14.0067 |
| Density | 1.2506 grams/litre |
| Atomic Radius | 155 pm |
| Ionization Energy | 14.534 eV |
| Covalent Radius | 71 pm |
| Ionic Radius | 0.171nm (-3) ; 0.011 (+5) ; 0.016 (+3) |
| Electronic Gain Enthalpy | Almost Zero |
| Electron Negativity | 3.04 |
| Electron Affinity | 7 kJ/mol |
| Melting Point | −209.86 °C (−345.8 °F) |
| Boiling Point | −195.8 °C (−320.4 °F) |
Chemical Properties of Nitrogen
| Atomic Number | 7 |
| Group | 15 |
| Period | 2 |
| Block | p |
| Electronic Configuration | 1s22s22p3 |
| Combustion | It is non-flammable |
| Chemical Reactivity | It is a non-reactive element |
| Valency of Element | 3 |

Different States of Nitrogen
At room temperature, nitrogen is a gas. However, when it is exposed to an extremely cold temperature, it will liquify. Once in liquid form, it will come to a boil when exposed at room temperature.
Once liquid nitrogen heats up, it turns back to its gaseous state. Once you place cold liquid nitrogen in a container and leave it at room temperature, the gas will create pressure, causing the container to explode.
What are the common uses of nitrogen?
Chemical industry
- Nitrogen plays a vital role in the chemical sector. It is used for creating nylon, nitric acid, dyes, fertilizers, and explosives.
- To use nitrogen for making such products, it must be exposed to hydrogen to create ammonia through the process called the Haber process.
Creating an unreactive atmosphere
- Nitrogen is helpful in creating an unreactive atmosphere, which is used in food preservation and the electronic sector when producing diodes and transistors.
Annealing of stainless steel
- A huge quantity of nitrogen is used to anneal stainless steel and steel products.
- It is the process by which steel is heat treated, making it easier to work with.
Refrigerant
- Nitrogen in liquid form is used as a refrigerant, which is helpful in storing cells such as sperm and egg cells for medical research and reproductive purposes.
- It is also helpful in the food industry because it freezes foods to retain essential elements such as flavor, color, moisture, and texture.
Enhances oil recovery
- Nitrogen enhances oil recovery, specifically crude oil and the petroleum industry as a whole.
Reduction of fire hazards
- Nitrogen is useful in an inert atmosphere because of its ability to greatly reduce fire hazards in aircraft fuel systems.
Light bulb
- Nitrogen can be used as a replacement for argon gas, which is used in light bulbs.
Flammable/explosive protection
- Nitrogen plays an important role in protecting flammables and solid and liquid explosives from getting into contact with air.
Price of Nitrogen
The cost of nitrogen varies depending on supply and demand as well as whether it’s in pure form or not. For pure nitrogen, the cost is $0.4/100 gram. If you’re going to purchase in bulk, the cost is around $1/100 grams.
Interesting facts about nitrogen
- In a living organism, about 2.5% of the total body weight is nitrogen.
- Don’t you know that many living things’ molecules have nitrogen? In fact, nitrogen is the fourth most abundant chemical element in the human body.
- Nitroglycerin, a nitrogen compound, can be used to manage life-threatening conditions such as angina and other heart-related conditions.
- Nitrogen ranked seventh on the list of the most abundant elements in the universe.
- Nitrogen is non-toxic in its liquid form.
- Don’t you know that the level of nitrogen on Earth is far greater than on Mars?
- Don’t you know that nitrogen makes a good blanketing gas primarily because of its inert properties?
- Saturn’s largest moon’s atmosphere contains more than 98% nitrogen.
- Nitrogen is also called “burnt” as well as “dephlogisticated air” because if you remove oxygen from the air, basically what is left is nitrogen.
- Bacteria in the soil can fix nitrogen into a form that is useful for living organisms like plants and animals. They use it to create proteins and amino acids.
- Don’t you know that nitrogen plays an essential role in the color of the aurora? It is responsible for colors like blue-violet, blue-green, and orange-red.
Pictures of Nitrogen


Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What makes nitrogen an essential element?
Nitrogen is an integral component of all life forms. It can be seen in cells and it is needed to form living molecules like proteins, amino acids, and even DNA. Nitrogen is necessary in making chlorophyll, a vital component in photosynthesis needed to create food in plants.
Q2. What is nitrogen’s common elemental form?
The common elemental form of nitrogen is dinitrogen. It comprises about 78% of the breathable atmosphere. It is not that reactive because of the triple bond strength.
Q3. Why does nitrogen not react that easily?
Nitrogen has high bond energy, which makes the activation energy for any reaction extremely high. Hence, the very reason why nitrogen is relatively inert to almost all reagents under normal conditions.
Q4. Is nitrogen safe to drink?
Nitrogen is non-toxic, but it does not necessarily mean it is completely safe. Nitrogen in liquid form can cause severe damage to the skin and vital organs in the body, especially when ingested or mishandled. It is linked with liquid nitrogen’s extremely low temperature.
Q5. Can soil bacteria transform nitrogen?
Nitrogen, although inert, can be transformed by soil bacteria in a way that flora and fauna are capable of using it to create proteins and amino acids.
References
- https://www.britannica.com/science/nitrogen
- https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/7/nitrogen
- https://www.chemicool.com/elements/nitrogen.html
- https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/n.htm
- https://www.thoughtco.com/nitrogen-facts-606568
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nitrogen
- https://www.nue.okstate.edu/Crop_Information/Nitrogen_Facts1.htm
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Nitrogen
- https://byjus.com/chemistry/nitrogen/
- https://education.jlab.org/itselemental/ele007.html