What is Selenium?
Selenium belongs to the non-metal group. It shares the same physical and chemical characteristics as tellurium and sulfur. It appears in allotropic forms with red amorphous powder as the most popular form. Find out more about this precious chemical element here.
Where is Selenium obtained?
A few minerals contain selenium. The majority of produced selenium came from anode muds during the refining of copper. The muds are roasted with sodium carbonated or sulfuric acid. It can also be smelted with sodium carbonate.

Selenium is also present in the earth’s crust but is very minute when compared with other chemical elements. The human body also has a small amount of selenium. Rare minerals like the crook site and clausthalite also have selenium.
Countries, where selenium is commonly mined, include Canada, Japan, Belgium, and the United States.
History of Selenium
The discovery of selenium is dated back to 1817 at Stockholm by Jöns Jacob Berzelius. He contributed to sulfuric acid works and at that time one thing that captured his interest was the red-brown sediment that settled at the bottom of the chamber.

At that time, he thought that it was tellurium because if you bring it to heat it produces a distinct radish-like odor. He, later on, realized that it was in fact a new element, thus, giving birth to what is now known as selenium.
Classification, Properties, and Characteristics of Selenium
Selenium is classified as chalcogen, which means that it belongs to the oxygen family group. It has three allotropes (physical forms). Selenium is reactive, thus, the reason why it is rare to find pure selenium in nature. It is also quite stable because of its tendency to bond. It does not corrode easily.
Lewis Dot Structure of Selenium

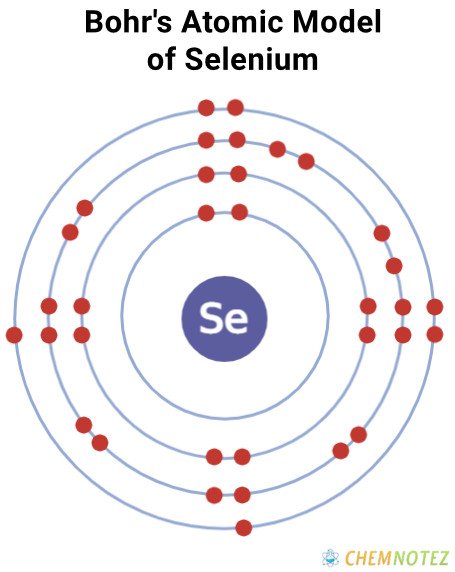
Bohr’s Atomic Model of Selenium
Atomic Data of Selenium
Physical Properties of Selenium
| Color | Silvery/Red |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Colorless |
| Atomic Mass | 78.971 |
| Weight | 78.96 |
| Density | 4.809 |
| Atomic Radius | 1.90 Å |
| Ionization Energy | 940.963kJ mol−1 |
| Covalent Radius | 1.18Å |
| Ionic Radius | 0.198 nm (-2) ; 0.042 nm (+6) |
| Electronic Gain Enthalpy | 194.965 kJ mol−1 |
| Electron Negativity | 2.55 |
| Electron Affinity | 194.965 kJ mol−1 |
| Melting Point | 220.8°C, 429.4°F, 494 K |
| Boiling Point | 685°C, 1265°F, 958 K |
Chemical Properties of Selenium
| Atomic Number | 34 |
| Group | 16 |
| Period | 4 |
| Block | p |
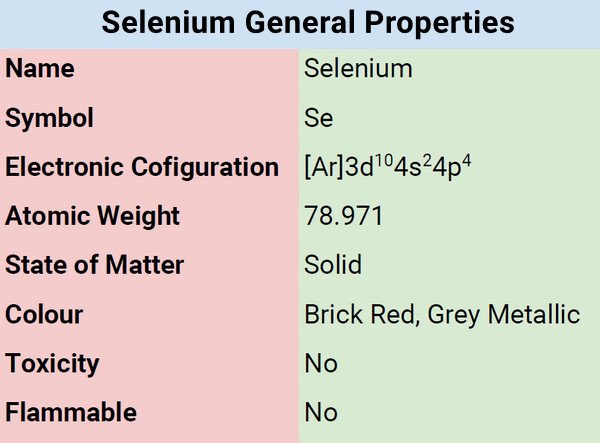
| Electronic Configuration | [Ar] 3d104s24p4 |
| Combustion | Non-combustible |
| Chemical Reactivity | Fairly Reactive |
| Valency of Element | -2, 4, and 6 |
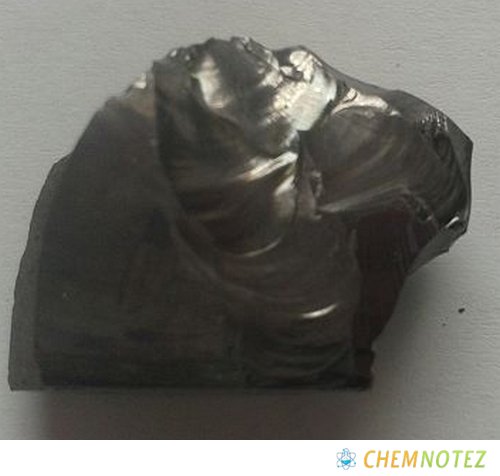
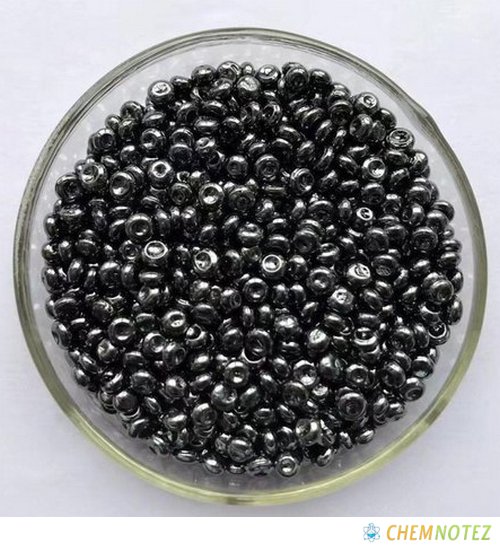
Different States of Selenium
Selenium is solid at room temperature, specifically between 68 and 72 degrees. It melts once it reaches 220.8 degrees Celsius. it comes in three physical forms. In a normal state, selenium is red, amorphous powder-like substance. It will take on a vitreous form when melted characterized by a black and lustrous irregular shape. If you slowly heat selenium, it forms a gray powder, which is the most stable form.


Uses of Selenium
- Selenium is used as an additive in making glass. It is responsible for giving glass its color. Some give glasses a deep red color while other selenium compounds decolorize glasses.
- Selenium is useful in reducing the transmission of sunlight in architectural glass. It gives the glass a bronze tint.
- It is used to give pigments to paints, plastics, and ceramics.
- Selenium is useful in solar cells, photocells, and photocopiers. Thanks to its ability to convert light to electricity (photovoltaic action).
- Selenium has the ability to convert AC to DC electricity, thus the reason it is used in rectifiers.
- Selenium in the form of selenium sulfide is one of the components of anti-dandruff shampoo because of its ability to kill fungus.
- It is used to make stainless steel.
- Selenium serves as a catalyst in various chemical reactions.
- Selenium is added to copper and iron-based metals to significantly improve their machinability.
Price of Selenium
The cost of selenium is dependent on supply and demand. Pure selenium costs around $60 per 100 grams. If you purchase in bulk, the price is lower, usually in the range of $6 to $7 per 100 grams.
Interesting facts about Selenium
- Don’t you know that selenium derived its name from the Greek word “Selene”, which means “moon?” In Greek mythology, Selene is the goddess of the moon.
- Some food sources contain a high level of selenium such as Brazil nuts. In fact, the amount of selenium in a single Brazil nut is enough to meet the body’s daily need for selenium. Other valuable sources of selenium are meats, mushrooms, and cereals.
- Don’t you know that about 2,000 tons of selenium are extracted yearly worldwide?
- China is the largest refiner of selenium in 2018 producing over 1 million tons, according to USGA.
- The very first compound used in the blue light of LEDs is zinc selenide.
- Although selenium is considered an essential micronutrient, taking it in a high amount can be extremely toxic to health.
- Don’t you know that in 2009, 21 ponies participated in the Polo event diet because of selenium poisoning? It is linked to the incorrect dosing of mineral supplements from a compounding pharmacy.
- Don’t you know that a deficiency in selenium can increase the risk of certain diseases such as diabetes, HIV, and cancer?
- A deficiency of selenium in animals may increase the risk of reproductive system dysfunction and slow growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What can possibly happen if selenium reacts with oxygen?
If selenium burns in the air, it will display a blue-colored flame forming solid selenium dioxide.
Q2. Can we live without selenium?
Selenium in the right amount is beneficial for the body. If the body does not get an adequate level of selenium, it could lead to certain conditions, especially the ones related to thyroid functions. Examples are Grave’s disease and Hashimoto’s disease.
These conditions trigger the body to form antibodies and will attack the thyroid gland. It will eventually lead to conditions like hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid).
Q3. How much selenium is toxic to humans?
The therapeutic dose of selenium is no more than 150µg. the maximum safe level of selenium is around 400µg as per the Dietary Supplements Regulations 1985. If it exceeds the safety level, expect obvious signs of toxicity.
Q4. What is the best form of selenium?
If you are looking for the best form of selenium, the answer would be selenomethionine because it has a superior absorption rate.
Q5. Is selenium good for the skin?
Selenium is one of the components of many skincare products because it is gentle on the skin. It keeps the skin firm, healthy, and protected. It has the ability to block free radical damage, thus, preventing premature skin aging such as the formation of fine lines and wrinkles. It also protects the skin from inflammation, hyperpigmentation, and the damaging rays of the sun.
References
- https://www.thoughtco.com/interesting-selenium-facts-609110
- https://www.livescience.com/31972-selenium.html
- https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/34/selenium
- https://www.britannica.com/science/selenium
- https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/se.htm
- https://www.factsjustforkids.com/chemistry-facts/selenium-facts-for-kids/
- https://www.chemicool.com/elements/selenium.html
- https://chemistrydictionary.org/selenium/
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-selenium-uses-facts-properties-discovery.html
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Selenium