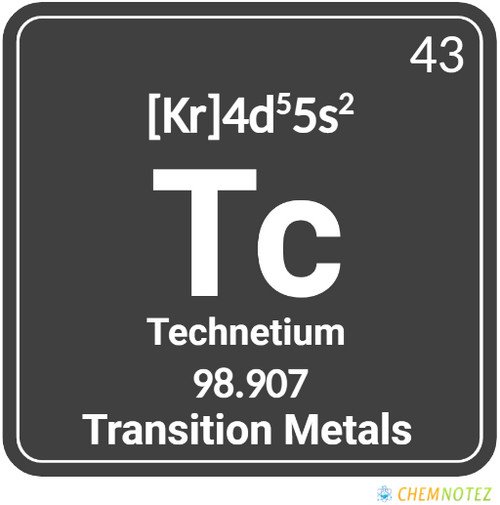
What is Technetium?
Technetium belongs to the transition metal group characterized by its silvery-gray color. It dissolves in acids, specifically aqua regia/nitro-hydrochloric acid, concentrated sulfuric acid , and nitric acid. It is not soluble in hydrochloric acid. When exposed to air, it gradually tarnishes. It’s a pretty interesting element and you will know more about it in this article.
Where is Technetium obtained?
Almost all technetium is produced synthetically/artificially. The natural source of technetium is a product of the spontaneous fission of uranium ore and thorium ore. Technetium was found in the spectrum of M, N, and S-type stars.
History of Technetium
Technetium was the very first chemical element produced synthetically. It is known as element 43 and is predicted to be created eventually on the basis of the noticeable gap in the periodic table of elements. It was in 1925 when it was erroneously reported as masurium. The breakthrough came in 1937 when technetium was discovered and artificially produced by Perrier and Segre in Italy.

Classification, Properties, and Characteristics of Technetium
Technetium is a silver-gray metal that when exposed to moist air, slowly tarnishes. When in powder form, technetium burns in oxygen and form heptoxide. Its chemical symbol is Tc and classified as a transition metal. It is located between manganese and rhenium and belongs to group 7 in the periodic table of elements. Its properties are somewhat the same as the adjacent elements.
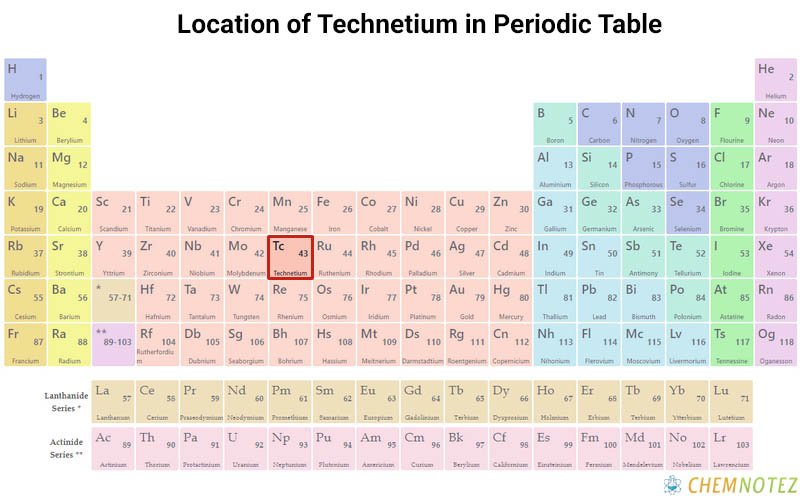
Lewis Dot Structure of Technetium
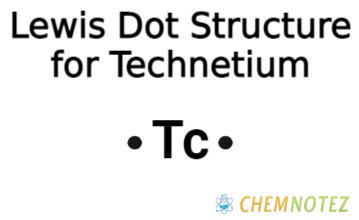
Bohr’s Atomic Model of Technetium
Atomic Data of Technetium
Physical Properties of Technetium
| Color | Silvery |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Tasteless |
| Atomic Mass | (99) g.mol -1 |
| Weight | 97 g.mol-1 |
| Density | 11.5 g.cm-3 at 20°C |
| Atomic Radius | 2.16 Å |
| Ionization Energy | 702.41kJ mol−1 |
| Covalent Radius | 1.38Å |
| Ionic Radius | 2.10 |
| Electronic Gain Enthalpy | 53.07 kJ mol−1 |
| Electron Negativity | 1.9 |
| Electron Affinity | 53.07 kJ mol−1 |
| Melting Point | 2157°C, 3915°F, 2430 K |
| Boiling Point | 4262°C, 7704°F, 4535 K |
Chemical Properties of Technetium
| Atomic Number | 43 |
| Group | 7 |
| Period | 5 |
| Block | D |
| Electronic Configuration | [Kr]4d55s2 |
| Combustion | Not Flammable |
| Chemical Reactivity | Somewhat Reactive |
| Valency of Element | +4, +6, or +7 |
Different States of Technetium
As a transition metal, technetium is solid at room temperature. Its usual oxidation states are +4, +5, and +7. It exists as a pertechnetate ion under oxidizing circumstances.
Uses of Technetium
- It acts as a corrosion inhibitor for steel, but corrosion protection is only applicable to closed systems.
- Technetium acts as a superior superconductor.
- One of the isotopes of technetium is used in tracer work.
- Technetium is used in various medical radioactive isotope tests and diagnostic studies.
- Technetium-99 is used for equipment calibration.
- It functions as a catalyst, which is pretty much the same as the way palladium and rhenium are used.
- Some of its compounds are used in manufacturing photoelectric nuclear batteries.
- Technetium can possibly be used in opto-electric nuclear batteries.
- It can be used to map the circulatory system.
Price of Technetium
The cost of technetium fluctuates depending on supply and demand. However, technetium is only commercially available to O.R.N.L. permit holders. The price is around $60/g.
Interesting facts about Technetium
- Don’t you know that technetium comes from the Greek word “technetos”, which means “artificial?”
- It is the lightest element that contains all radioactive isotopes.
- In the original Mendeleev Periodic Table, technetium was missing.
- Technetium is a radioactive metal, which means that it is toxic to humans.
- when handling technetium, one must wear safety gloves.
- Technetium has an odd number of protons, thus, explaining why it is radioactive while its neighboring elements are not.
- Technetium was discovered in red giants in 1952, which proves that stars produce heavy elements.
- Technetium in powder form burns in oxygen.
- Technetium is a transition metal, but it does not form cations. What it forms are covalent bonds.
- Technetium does not dissolve in hydrochloric acid.
- Technetium is the first man made chemical element.
- Don’t you know that technetium is one of the elements that has already been predicted even before its discovery? It is because of the existing pattern in Mendeleev’s periodic table of elements.
- Technetium was previously named masurium.
- Technetium, when discovered in 1937, was actually found in a molybdenum sample.
- Technetium is unstable.
- Technetium is one of the elements that are not usually found in the human body.
- It is the only below uranium that doesn’t exist on the earth’s crust.
- Technetium is one of the man made or artificially created chemical elements that are produced using a particle accelerator.
- The presence of technetium in the stars can be detected by analyzing the light it produced.
- Technetium has no commercially important compounds.
- When technetium-99m is used in a medical setting, healthcare workers bring a molybdenum-99 container because it is actually a form of molybdenum-99.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What does technetium react with?
Technetium is somewhat reactive. It gradually reacts with acid and air.
Q2. What are the dangers of technetium?
Technetium is primarily used as a radioactive tracer and so utmost precautions must be done when handling this element. Failure to handle it properly may cause allergic reactions, tearing, and anaphylaxis. The radioactive material itself is carcinogenic.
Q3. Why is technetium unstable?
One of the reasons why technetium is unstable is because most of its isotopes or forms have excess neutrons.
Q4. Is technetium harmful to kidneys?
When technetium is used medically such as in the case of radiation, there is an acceptable radiation dose. When used the right way, it will not cause any toxic effects. Around 90% of it is eliminated through excretion within 24 hours.
Q5. Is technetium a good conductor?
Technetium belongs to the metal group, and like the typical characteristics of metal, technetium is a very good conductor of heat and electricity.
References
- https://www.livescience.com/34774-technetium.html
- https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/43/technetium
- https://www.britannica.com/science/technetium
- https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/tc.htm
- https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/Community/educationalresources/PeriodicTable/Technetium/
- https://www.chemicool.com/elements/technetium.html
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/element/Technetium
- https://byjus.com/chemistry/technetium/
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/technetium-facts-properties-discovery.html
- https://sciencenotes.org/technetium-facts-atomic-number-43-element-symbol-tc/