What is Yttrium?
Yttrium is a rare earth metal that belongs to group 3 in the periodic table. It is silvery white, ductile, and quite soft. It’s relatively stable in the air but can get oxidized once it reaches a certain temperature level. More about yttrium is discussed below.
Where is Yttrium obtained?
Although yttrium was discovered in Scandinavia, it is ironic to know that yttrium is more abundant in other places such as India, Russia, China, Australia, and Malaysia. Yttrium is found in rare earth minerals, although it was never found in the earth’s crust as a free element. During the Apollo moon missions, the gathered lunar rocks have yttrium. It is also found that yttrium is present in the human body but in a minute amount. It is usually found in the kidneys, bones, and liver.
History of Yttrium
Carl Axel Arrhenius, a Swedish army lieutenant and chemist explored a quarry near Ytterby and was able to discover an odd black rock in 1787. at that time, he thought he discovered a new mineral that has tungsten and so he sent the rock to Johan Gadolin, who is a chemist and mineralogist based in Finland.

The latter thoroughly studied the specimen, and he, later on, named it gadolinite. Another study made by Carl Gustaf Mosander in 1843 involved yttrium samples and found out that it contains three oxides, but at that time it was called terbia, erbia, and yttria.
These oxides are now known as yellow terbium oxide, white yttrium oxide, and rose-colored erbium oxide. In 1878, another oxide was discovered – ytterbium oxide.
Classification, Properties, and Characteristics of Yttrium
Yttrium is a silvery metal, quite soft. Its color changes from dark gray to black when in powder form. It is innately shiny but gets dark when exposed to light. It shares the same properties as other rare earth metals. It is stable in the air. It does not have any distinct taste or odor.
Lewis Dot Structure of Yttrium

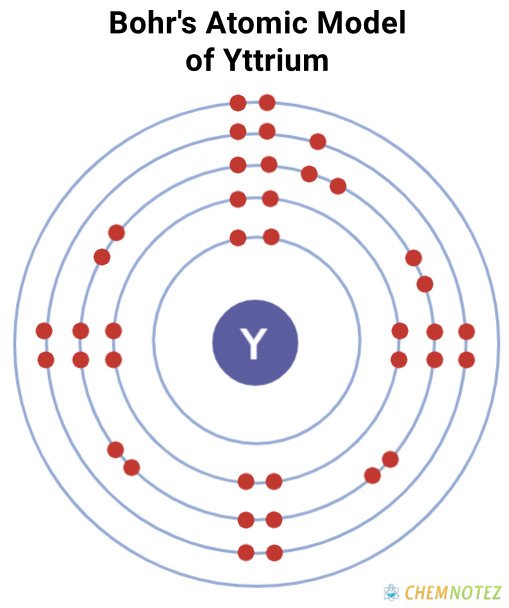
Bohr’s Atomic Model
Atomic Data of Yttrium
Physical Properties of Yttrium
| Color | Silvery |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Tasteless |
| Atomic Mass | 88.906 |
| Weight | 88.906 |
| Density | 4.47 |
| Atomic Radius | 2.32Å |
| Ionization Energy | 599.878kJ mol−1 |
| Covalent Radius | 1.76Å |
| Ionic Radius | 240 pm |
| Electronic Gain Enthalpy | 29.621kJ mol−1 |
| Electron Negativity | 1.22 |
| Electron Affinity | 29.621kJ mol−1 |
| Melting Point | 1522°C, 2772°F, 1795 K |
| Boiling Point | 3345°C, 6053°F, 3618 K |
Chemical Properties of Yttrium
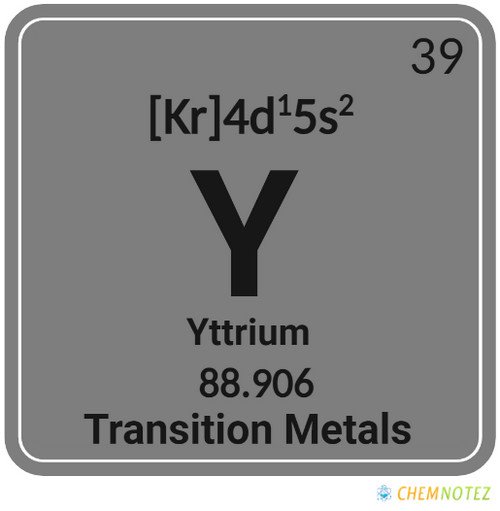
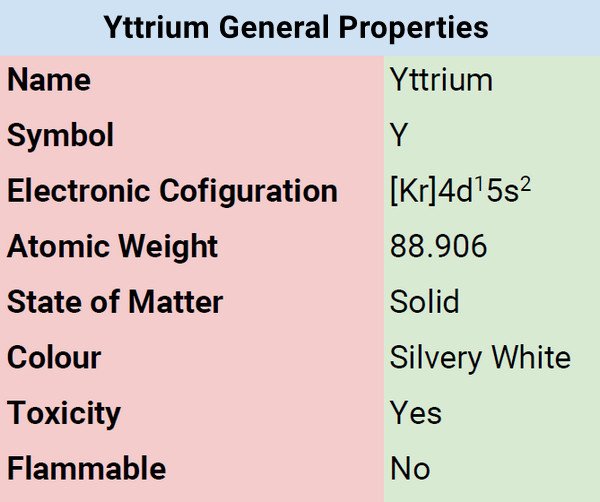
| Atomic Number | 39 |
| Group | 3 |
| Period | 5 |
| Block | d |
| Electronic Configuration | [Kr] 4d15s2 |
| Combustion | Flammable in powder form |
| Chemical Reactivity | Highly Reactive |
| Valency of Element | 3 |
Different States of Yttrium
As a transition metal, yttrium is solid at room temperature. It melts once the desired temperature is reached. Its oxidation state is +3 and it behaves like the usual rare-earth element.

Uses of Yttrium
- Television models before the flat-screen era uses yttrium oxide along with europium and their role is to give red color on color-tv sets.
- Yttria, yttrium oxide is added to zirconia oxide to create an alloy to stabilize zirconia’s crystal structure. What yttria does is it locks in that particular zirconia structure making zirconia products (e.x ceramic) with ultra-toughness perfect to use even at high temperatures. Usually, those ceramic products are used in electronics and medical implants.
- It is used to simulate diamonds and other gemstones. It is specifically used to create synthetic garnets using yttrium-aluminum composite.
- Yttrium aluminum garnets are used to amplify light in industrial lasers.
- Microwave filters use yttrium iron garnets.
- Yttrium is also used in radar communication technology.
- Phosphors, a substance used in large display screens and cellphones use yttrium.
- Yttrium-90, a radioactive isotope is used as a part of radiation therapy, which is helpful in the treatment of some types of cancers such as liver cancer.
- It is used as an alloying agent to further strengthen magnesium and aluminum alloys.
- Yttrium oxide is usually added to glass to create lenses for cameras to make them resistant to heat and shock.
- Yttrium acts as a deoxidizer for vanadium and other non-ferrous metals.
- It acts as a catalyst in ethylene polymerization.
Price of Yttrium
The cost of yttrium is dependent on supply and demand, and since it is one of the rare elements, expect its price to be on the high end. Pure yttrium costs around $430 per 100 grams. You can save money if you purchase in bulk.
Interesting facts about Yttrium
- Don’t you know that the moon has a higher concentration of yttrium than the earth? A sample of rock from the moon from the Apollo missions was identified as yttrium and on analysis, it was found that it has 200 ppm of yttrium, which is way higher than the one found on earth’s crust, which only has 30 ppm.
- Don’t you know that a combination of yttrium and aluminum was used to create diamond imitation and is widely used in jewelry making? Although today, it is replaced by cubic zirconia.
- Don’t you know that spark plugs used in combustion engines are coated with yttrium?
- The chemical element yttrium was named after Ytterby, a village in Sweden that has an adjacent quarry rich in minerals like feldspar, and quartz, among others.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What does yttrium react with?
Yttrium is reactive with water. It decomposes and paves the way for the release of hydrogen gas. It is also reactive with acids. If you shave or turn yttrium, there is a possibility of ignition in the air, especially when it reaches over 400 degrees Celsius. if you divide the yttrium into small pieces, it will become unstable in the air.
Q2. What are the dangers of yttrium?
If you breathe in the yttrium, it can lead to lung irritation. You will experience respiratory-related symptoms like coughing and shortness of breath. If the exposure to yttrium goes on for a long period of time without proper gear and protection, there is a possibility of pneumoconiosis or scarring of the lungs. It can also damage the liver. Another danger of yttrium is when it is in powder form it becomes flammable. It is considered a fire hazard.
Q3. What country has the biggest yttrium reserves?
China, by far, has the largest yttrium reserves.
Q4. Is yttrium a pure substance?
After a thorough analysis made by experts, it was found that yttrium was not a pure substance. It was actually a mixture of different substances.
Q5. What makes ytterbium unique?
Yttrium is unique in the sense that it is rare. Like the usual rare metals, it is quite soft and malleable. It is easily attacked by mineral acids. It oxidizes in air and gradually reacts with water.
References
- https://www.livescience.com/34564-yttrium.html
- https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/39/yttrium
- https://www.britannica.com/science/yttrium
- https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/y.htm
- https://www.chemicool.com/elements/yttrium.html
- https://www.thoughtco.com/yttrium-facts-606620
- https://www.sputtertargets.net/blog/uses-properties-facts-about-rare-earth-yttrium.html
- https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-yttrium-facts-classification-properties.html
- https://chemistrydictionary.org/yttrium/
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Yttrium