What is Silver?
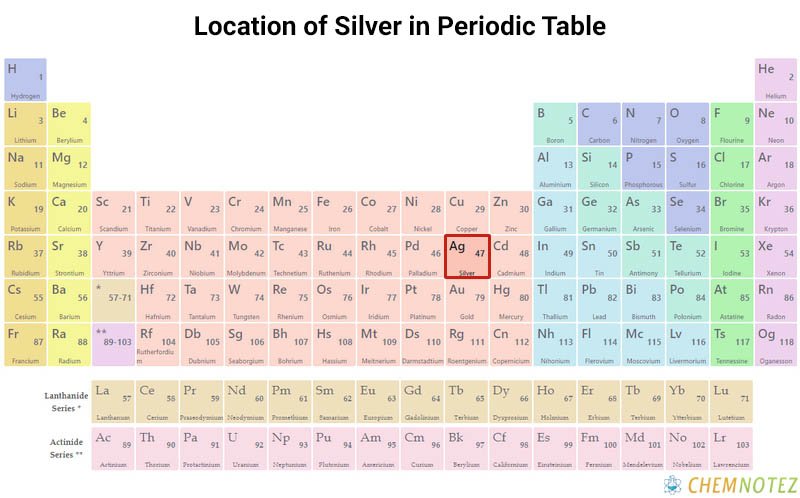
Silver belongs to group 11 in the periodic table of elements. It is known for its shiny white color and prized for its ornamental appeal and electrical conductivity. It’s located between copper and gold, which explains why its physical and chemical characteristics are between those two metals. More about this precious metal will be discussed below.
Where is Silver obtained?
Silver occurs in a natural state. P In other words, pure silver crystals or nuggets can be found in nature. Electrum is a naturally occurring alloy of silver and gold. Silver is frequently found in copper, zinc, and lead ores. Peru is the second-largest producer after Mexico. Silver is also produced in Russia, Australia, the United States, and Canada. Approximately two-thirds of the silver produced today come from byproducts of zinc, lead, and copper mining industries.

History of Silver
One of the first five metals to be discovered and utilized by mankind, silver holds a special spot in the chemical elements’ history. Silver mining began about 5,000 years ago. Around 3,000 BCE, silver was first mined in Anatolia, which is now part of modern-day Turkey. Early civilizations in the Near East and Ancient Greece benefited from the precious metal’s prosperity. Unfortunately, the discovery of silver is not associated with or linked to any person.
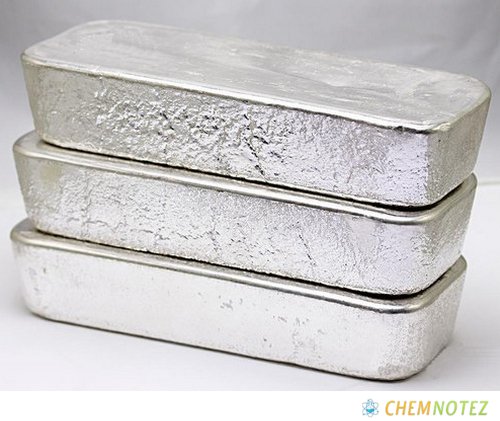

Classification, Properties and Characteristics of Silver
Silver belongs to the precious metals group, along with gold and the metals from the platinum group. Silver has been used for many years to make coins, ornaments, and jewelry due to its relative rarity, dazzling white color, ductility, malleability, and ability to resist oxidation when exposed to air. Of all metals, silver has the highest known thermal and electrical conductivity. In oxygen and water, silver is stable, but in the air, it tarnishes due to a reaction with sulfur molecules that results in the formation of a black sulfide coating.
Lewis Dot Structure of Silver

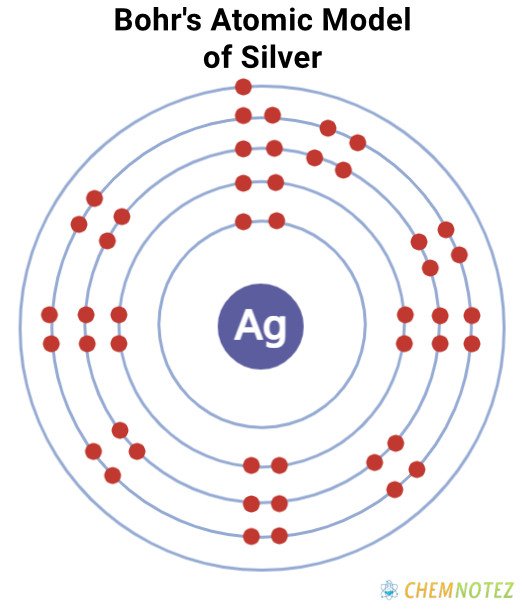
Bohr’s Atomic Model of Silver
Atomic Data of Silver
Physical Properties of Silver
| Color | White Lustrous |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Taste | Sweet and Sour Taste |
| Atomic Mass | 107.868 |
| Weight | 107.868 |
| Density | 10.5 |
| Atomic Radius | 2.11 Å |
| Ionization Energy | 730.995 kJ mol−1 |
| Covalent Radius | 1.36Å |
| Ionic Radius | 0.126 nm |
| Electronic Gain Enthalpy | 125.624 kJ mol−1 |
| Electron Negativity | 1.93 |
| Electron Affinity | 125.624 kJ mol−1 |
| Melting Point | 960.8 °C (1,861.4 °F) |
| Boiling Point | 2,212 °C (4,014 °F) |
Chemical Properties of Silver
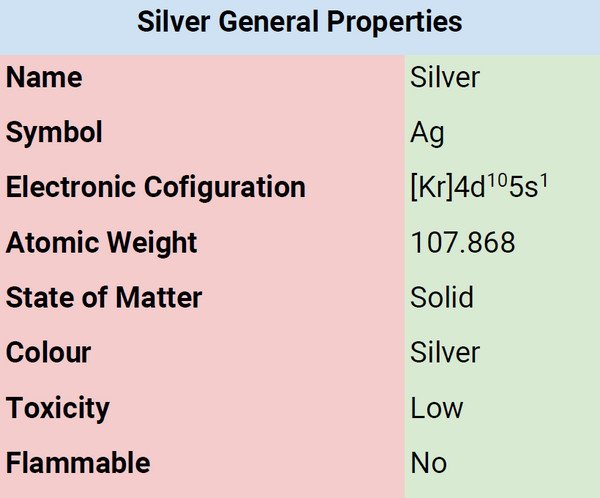
| Atomic Number | 47 |
| Group | 11 |
| Period | 5 |
| Block | d |
| Electronic Configuration | [Kr]4d105s1 |
| Combustion | Flammable in dust and powder form |
| Chemical Reactivity | Not very reactive |
| Valency of Element | 1 |
Different States of Silver
Silver is a precious metal, which is solid at room temperature. It exists in various oxidation states with +1 as the preeminently significant oxidation state.
Uses of Silver
- Silver has antimicrobial properties, which makes it perfect for water and air conditioning filtration systems.
- Silver is used for solar energy applications.
- It is useful for mirror coatings because of its ability to reflect visible light.
- Silver is used as a currency.
- It is exceptionally shiny, which is the reason why it is commonly used to make jewelry pieces and silverware.
- Some electronics used silver materials.
- It is used in photography.
- Microscopes, telescopes, and solar cells used silver.
- Silver iodide is one of the chemicals used for cloud seeding. Once introduced to clouds, it produces rain. It is also used to control hurricanes.
- Silver is used in dental alloys.
- Printed circuits are used to make silver paints.
- Silver compounds, specifically silver bromide and iodide have been helpful in photography history because of their particular property, which is sensitivity to light.
- In digital photography, silver salts are used to produce high-quality images and protect it from unauthorized copying.
- Silver is known for its antibacterial properties. A particular compound, silver nanoparticles are used in textile to prevent bacteria from forming, especially if you sweat. That is why some clothing materials are expensive because of their antibacterial properties.
- Silver (E174) is used as a food coloring.
Price of Silver
The cost of silver fluctuates depending on supply and demand. Pure silver costs around $120 per 100 grams, but you can save money if you buy it in bulk.
Interesting facts about Silver
- Ag is the chemical symbol for silver. It comes from Argentum, the Latin word derived from argunas, which means “shining.”
- Don’t you know that United States coins minted before 1965 contain 90% silver?
- Silver is non-toxic, which makes it a suitable food decoration. However, silver salts are toxic.
- Silver has germicidal properties, which makes it effective in killing bacteria.
- Silver is an excellent electric conductor. In terms of electrical conductivity, silver ranks 100 in the range of 0 to 100. It is followed by copper and gold.
- Sterling silver is the commonly encountered silver form. It is made from 92.5% silver and the rest is copper.
- Don’t you know that a grain of silver can be pressed into 150 times thinner sheets than the usual sheet of paper?
- There are a few highly explosive silver compounds such as silver amide, silver fulminate, silver oxalate, silver acetylide, and silver azide.
- Don’t you know that the official currency of the UK, the pound Sterling originally equal to a pound of silver?
- About 30% of silver production, specifically silver nitrate was used for photography.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Can silver be destroyed?
Tarnish in silver material can be destroyed easily. It doesn’t destroy silver at all. That is why it belongs to the precious metal group.
Q2. Who uses silver the most?
One of the countries that use silver the most is the United States. It uses around 21.6% of the total production of silver in the world.
Q3. Is silver toxic to humans?
Silver is extremely low in toxicity. It possesses little to minimal risk.
Q4. Does fire affect silver?
There is a serious issue with regard to fire damage related to silverplate and sterling silver. The fire caused by silver material creates a black, greasy film. The soot must be washed off right away as it can significantly affect the state of the metal.
Q5. How is silver used in medicine?
Silver has medical significance. It is commonly used to dress wounds, as an antibiotic coating, as a component of medicinal creams, and as one of the components used for making medical devices.
References
- https://www.britannica.com/science/silver
- https://www.thoughtco.com/interesting-silver-element-facts-603365
- https://www.rsc.org/periodic-table/element/47/silver
- https://www.chemicool.com/elements/silver.html
- https://www.livescience.com/37040-silver.html
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Silver
- https://www.lenntech.com/periodic/elements/ag.htm
- https://www.ducksters.com/science/chemistry/silver.php
- https://sites.dartmouth.edu/toxmetal/more-metals/silver-metal-of-many-faces/the-facts-on-silver/
- https://byjus.com/chemistry/silver/